In the vast, interconnected web of life, there exists an often overlooked element that silently shapes the very foundation of our existence. Soils, those seemingly unremarkable layers of earth that encompass our planet, harboring a hidden world of untold beauty and complexity, hold within them the secrets to the sustainability and survival of countless organisms.
With its all-encompassing embrace, soil forms a vital link between the lithosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere, orchestrating a delicate symphony of interactions that influence the health, diversity, and resilience of our planet's ecosystems. The wonders of soil lie not only in its physical composition but also in the myriad of intricate dynamics it fosters.
Rich in organisms, both macroscopic and microscopic, soil teems with life that continuously interacts and metamorphoses, sculpting its unique structure and nourishing its inhabitants. Fungi thread through its depths, forming intricate networks that provide access to vital nutrients for plants. Nematodes, microscopic roundworms, silently navigate the labyrinthine spaces, both predator and prey, playing their roles in the intricate soil food web.
Time and again, the importance of soil in shaping human history has been demonstrated through civilizations that have thrived or crumbled based on the fertility and management of their soils. The critical role of soil in sustaining agricultural systems, providing food security, and mitigating climate change is now more urgent than ever before. As we delve into the ethereal realm beneath our feet, we unravel the secrets of soil and gain a deeper understanding of the profound impact it has on our environment.
The Hidden Life Beneath Our Feet: Unveiling the Secrets of Soil Microorganisms

Discovering the enigmatic world thriving beneath the surface, this section reveals the intriguing and intricate realm of soil microorganisms. Delving into the depths unseen, we expose the concealed life forms that play a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance of our soil ecosystems.
Unimaginably diverse and ubiquitous, soil microorganisms encompass a myriad of microscopic organisms that inhabit and interact within the soil environment. From bacteria and fungi to protozoa and nematodes, this concealed symphony of life collaborates to influence soil structure, nutrient cycling, and even plant health.
These microscopic inhabitants possess an immense power, silently shaping the soil's physical, chemical, and biological properties. They engage in a complex web of interactions, engaging in symbiotic relationships, decomposition of organic matter, and nutrient transformations, all of which profoundly impact soil fertility and ecosystem resilience.
Exploring the fascinating world of soil microorganisms unveils the intricate mechanisms through which they contribute to the health and sustainability of our natural environment. The recognition of their vital role in promoting agricultural productivity and conservation practices highlights the significance of studying and harnessing the potential of this hidden ecosystem.
By comprehending the remarkable diversity and functions of soil microorganisms, scientists and researchers strive to unlock innovative strategies for enhancing soil fertility, mitigating the impact of pollutants, and improving the overall health of ecosystems. Understanding these microscopic wonders serves as a foundation for sustainable land management practices and cultivating a deeper appreciation for the intricate harmony existing beneath our very feet.
Unveiling the Menace: Soil Erosion and its Dire Consequences for Food Security and Ecosystems
The degradation caused by soil erosion poses a significant threat to the stability of both food security and ecosystems. This alarming phenomenon, often underestimated and overlooked, can have devastating effects on agriculture, biodiversity, and overall environmental health. Understanding the root causes and potential solutions to soil erosion is crucial in safeguarding the future of our planet.
Soil erosion, the gradual removal and displacement of soil particles, can be driven by various factors such as water, wind, or human activities. This relentless force gradually strips away the fertile topsoil, depleting it of essential nutrients and organic matter necessary for healthy plant growth. As a result, agricultural productivity is severely compromised, leading to decreased crop yields and lower food availability for a growing global population.
Moreover, soil erosion also disrupts the delicate balance of ecosystems. The loss of topsoil often leads to increased sedimentation in water bodies, negatively impacting aquatic habitats and water quality. This sedimentation can smother aquatic organisms, destroy spawning grounds, and contribute to the decline of numerous plant and animal species. Additionally, soil erosion can exacerbate the occurrence of floods and landslides, further endangering human settlements and infrastructure.
| The Consequences of Soil Erosion: | Potential Solutions: |
|---|---|
| 1. Reduced agricultural productivity | 1. Implementing efficient soil conservation practices |
| 2. Increased water pollution | 2. Promoting sustainable land management techniques |
| 3. Biodiversity loss | 3. Reforestation and afforestation initiatives |
| 4. Increased risk of floods and landslides | 4. Establishing erosion control measures |
Addressing soil erosion requires a holistic approach that encompasses both sustainable land management practices on individual farms and broader policies at regional and national levels. By raising awareness about the severity of soil erosion and its cascading effects, we can foster a collective responsibility to protect the invaluable resource beneath our feet, ensuring food security, preserving biodiversity, and securing the future of our fragile ecosystems.
From Dust to Gold: Unveiling the Economic Potential of Soil

In this section, we will shed light on the untapped economic opportunities that lie beneath our feet. Soil, often overlooked and underestimated, holds immense potential for driving economic growth and prosperity. By exploring the hidden riches of soil, we can uncover a world of possibilities waiting to be discovered.
The Soil's Hidden Wealth:
Deep below the surface, soil harbors a wealth of resources that can be harnessed for economic gain. From minerals and organic matter to microorganisms and water, soil provides the foundation for agriculture, mining, construction, and various other industries. The economic potential of soil rests in its ability to support and sustain human activities, generating employment opportunities, innovation, and economic development.
Soil-Based Industries:
Understanding the economic potential of soil entails recognizing the industries that rely on its resources. Agriculture, for instance, heavily relies on fertile soil to cultivate crops and feed the growing population. With the increasing demand for food, the agricultural sector presents significant economic opportunities for farmers, agribusiness, and related industries. Likewise, soil-based industries such as mining and construction rely on the extraction and utilization of soil resources to fuel economic growth.
Innovation and Soil:
Innovation plays a crucial role in unlocking the economic potential of soil. From sustainable farming practices to soil management techniques, innovative approaches can optimize soil health, productivity, and sustainability. The integration of technology and soil analysis enables us to make informed decisions and maximize the economic benefits derived from soil. Only by embracing innovative solutions can we fully appreciate the economic value that lies within the realm of soil.
Expanding Economic Horizons:
Recognizing the economic potential of soil opens doors for new opportunities and sustainable development. By investing in research, education, and infrastructure, we can harness the potential of soil to create thriving economies while preserving the environment. Collaboration between governments, businesses, and communities is essential in unlocking the economic goldmine hidden beneath our feet.
In conclusion, understanding and leveraging the economic potential of soil are vital steps towards building a sustainable and prosperous future. By recognizing soil's hidden wealth, supporting soil-based industries, embracing innovation, and expanding economic horizons, we can transform soil from dust to gold, paving the way for economic prosperity and environmental sustainability.
Soil Pollution: Revealing the Detrimental Consequences of Contaminants
Within the context of the broader exploration into soil, it is imperative to delve into the topic of soil pollution, which encompasses the adverse effects caused by various contaminants present in the soil. This section aims to shed light on the significant ramifications of soil pollution, emphasizing the detrimental impacts it poses to the environment, agriculture, and human health.
| Consequences on the Environment | Impact on Agriculture | Effects on Human Health |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Disruption of ecosystems and loss of biodiversity | 1. Reduced crop yields and decreased food quality | 1. Increased risk of exposure to toxic chemicals |
| 2. Contamination of water sources through leaching | 2. Impaired soil fertility and nutrient imbalance | 2. Development of respiratory and cardiovascular diseases |
| 3. Accumulation of toxins in plants and animals | 3. Negative effects on soil microorganisms | 3. Adverse impacts on reproductive health |
| 4. Disruption of soil structure and erosion | 4. Increased reliance on synthetic fertilizers | 4. Higher risk of cancer and neurological disorders |
Soil pollution is caused by a myriad of contaminants, including heavy metals, pesticides, industrial wastes, and untreated sewage. These pollutants infiltrate the soil through various means, such as improper waste disposal, agricultural practices, and industrial activities. It is crucial to address this pressing issue through sustainable and responsible practices, including proper waste management, organic farming techniques, and pollution control measures, to mitigate the detrimental effects of soil pollution on our environment, food security, and overall well-being.
The Vital Connection: Exploring the Role of Soil in Water Filtration and Conservation
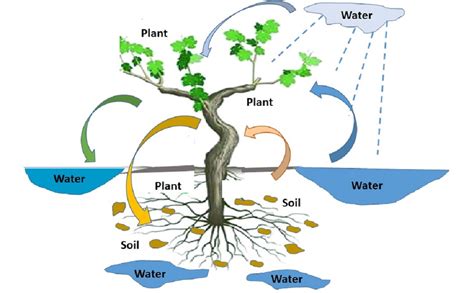
Understanding the intricate relationship between soil and water is key to comprehending the crucial role that soil plays in both water filtration and conservation. By delving into the interplay between these two elements, we can gain valuable insights into the mechanisms by which soil acts as a filter and reservoir, safeguarding our water resources and sustaining our environment.
When rainwater or any form of precipitation infiltrates the ground, it embarks on a remarkable journey through the soil layers. As this water percolates through the soil, it undergoes a series of intricate physical, chemical, and biological processes. These processes enable the soil to filter out impurities, contaminants, and excess nutrients, purifying the water before it reaches the underground aquifers or surface water bodies.
Not only does soil act as a natural filter, but it also plays a critical role in water conservation. The porous nature of soil allows it to absorb and store water, preventing runoff and facilitating groundwater recharge. By serving as a reservoir, soil imparts resilience to ecosystems, ensuring a sustainable supply of water for plants, animals, and human activities. Furthermore, the composition and structure of soil influence its water-holding capacity and infiltration rates, thereby influencing the movement and availability of water within the landscape.
The intricate symbiosis between soil and water is essential for maintaining a delicate balance in our environment. Soil plays a vital role in protecting water quality by actively removing harmful substances and pollutants from the water cycle. It acts as a natural barrier, preventing the contamination of water sources and safeguarding human health. Moreover, the conservation of water resources is intricately tied to the health and fertility of the soil. By preserving and enhancing soil quality, we can ensure a sustainable supply of clean water for both present and future generations.
In conclusion, exploring the profound connection between soil and water reveals the indispensable role of soil in water filtration and conservation. By comprehending the mechanisms and functions involved, we can foster sustainable practices that protect our precious water resources and preserve the health of our environment for years to come.
Preserving Soil Biodiversity: The Essential Need for Sustainable Land Management
In today's ever-changing world, the preservation of soil biodiversity has emerged as a crucial aspect of sustainable land management. Emphasizing the significance of maintaining a healthy and diverse soil ecosystem, this section aims to shed light on the vital role soil biodiversity plays in ensuring the long-term health and productivity of our planet.
The Diversity Within:
Soil biodiversity refers to the wide range of organisms inhabiting the soil, including bacteria, fungi, algae, protozoa, nematodes, earthworms, insects, and plant roots. These diverse organisms collectively form intricate networks and interactions within the soil ecosystem, contributing to essential ecological processes.
The Importance of Soil Biodiversity:
Soil biodiversity is crucial for numerous reasons. Firstly, it promotes nutrient cycling and the decomposition of organic matter, which are vital processes for enriching the soil with essential nutrients and promoting plant growth. The presence of diverse soil organisms also enhances soil structure, porosity, and water-holding capacity, thereby reducing soil erosion and improving water infiltration rates.
Furthermore, soil biodiversity plays a critical role in controlling pests and diseases, acting as a natural defense mechanism that minimizes the need for chemical pesticides. It also contributes to the maintenance of air quality by facilitating the breakdown of pollutants and the sequestration of carbon dioxide, helping combat climate change.
Threats to Soil Biodiversity:
Unfortunately, soil biodiversity faces various threats, primarily driven by unsustainable land management practices. Intensive agriculture, excessive use of chemical inputs, deforestation, urbanization, and land degradation contribute to the destruction of soil habitats and the loss of biodiversity. These detrimental practices disrupt the delicate balance within the soil ecosystem, leading to a decline in its functionality and resilience.
Preserving Soil Biodiversity through Sustainable Land Management:
Adopting sustainable land management practices is fundamental to preserving soil biodiversity. Implementing techniques such as organic farming, crop rotation, agroforestry, and the use of cover crops can help foster a diverse and resilient soil ecosystem. Conserving natural habitats, promoting soil conservation practices, and reducing the use of agrochemicals are also essential steps towards maintaining soil biodiversity.
In conclusion, recognizing the critical role of soil biodiversity and striving for sustainable land management practices are pivotal in ensuring the health and productivity of our soils. By preserving soil biodiversity, we not only safeguard the intricate web of life beneath our feet but also contribute to the overall well-being of our environment and planet.
Soil and Climate Change: Investigating the Feedback Loop

Exploring the intricate relationship between soil and climate change offers insights into a dynamic feedback loop that plays a crucial role in our planet's environmental balance. This section delves into the reciprocal interactions between soil and climate, highlighting the significant impact they have on each other.
Healthy Soil, Healthy Food: Examining the Link between Soil Quality and Nutritional Value
In this section, we will delve into the vital connection between soil quality and the nutritional value of the food we consume. Understanding the profound impact of soil health on the crops it nurtures is essential for comprehending how it ultimately affects our overall well-being.
Undoubtedly, the quality of soil plays a crucial role in determining the nutritional composition of the produce it yields. Soil enriched with organic matter, essential minerals, and a balanced pH level provides the perfect foundation for plants to absorb vital nutrients. These nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, are then transferred into the food we eat, contributing to its overall nutritional value.
The presence of beneficial microorganisms in healthy soil also influences the nutritional content of crops. These microorganisms assist in breaking down organic matter, releasing necessary nutrients for plants to assimilate. Additionally, they foster symbiotic relationships with plant roots, aiding in the absorption of micronutrients that are vital for human health. Thus, a diverse and thriving microbial community in soil contributes to the increased nutritional value of the food it helps produce.
Furthermore, soil quality influences the taste, aroma, and texture of the food we consume. Nutrient-rich soil contributes to a more robust flavor profile, resulting in an enhanced culinary experience. Additionally, crops grown in healthy soil tend to have a better texture and consistency, allowing for greater enjoyment when consuming them.
In conclusion, recognizing the link between soil quality and the nutritional value of food highlights the necessity for promoting healthy soil practices. By prioritizing sustainable farming methods, organic matter replenishment, and the preservation of beneficial microorganisms, we can ensure that the food we eat not only nourishes our bodies but also supports the overall well-being of our environment.
FAQ
Why is soil important for our environment?
Soil is essential for our environment as it serves as a home for various organisms, filters water, provides nutrients for plant growth, and helps with carbon sequestration.
How does soil affect plant growth?
Soil contains important nutrients and minerals that are necessary for plant growth. It also provides a stable foundation for plant roots and helps with water absorption and retention.
Can soil quality impact food production?
Absolutely, soil quality plays a vital role in food production. Healthy soil with proper nutrients ensures the growth of nutritious and high-quality crops, while poor soil quality can lead to low yields and lower nutritional value in crops.
What are some negative impacts that soil pollution can have?
Soil pollution can have various negative impacts. It can contaminate groundwater, reduce soil fertility, harm beneficial soil organisms, and even lead to the accumulation of toxic substances in our food chain.
What are some ways to improve soil health?
There are several ways to improve soil health. These include practicing organic farming methods, using cover crops, avoiding overuse of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, and implementing techniques like crop rotation and composting.



