Imagine a world where vast fields of golden, towering stalks emerge as a testament to the immense potential of maize. This vision encapsulates the captivating allure of this extraordinary crop, an unyielding source of sustenance and marvel that has been deeply ingrained in human history for countless generations. By delving into the intricate web of possibilities that corn cultivation presents, we unravel a tapestry of opportunities that extends far beyond mere sustenance.
As we embark on this exploration, it becomes apparent that corn agriculture is not solely confined to its traditional uses. Beyond its role in the culinary realm, corn possesses astounding versatility, emerging as a valuable resource in an array of industries. From biofuel production to packaging materials, and even the manufacturing of various biodegradable products, corn miraculously reveals its ability to be a sustainable and eco-friendly solution in the face of pressing global challenges.
By uncovering the manifold benefits of corn, such as its high nutritional value and adaptability to diverse climates, a compelling argument emerges for the widescale cultivation of this remarkable crop. With worldwide hunger persisting as a tragic reality, the remarkable yield and nutritional benefits of corn hold the potential to alleviate food scarcity and nourish those in need, fostering a more equitable and prosperous world for all.
Furthermore, the economic implications of corn farming cannot be underestimated. From providing livelihoods for countless farmers to bolstering international trade, the cultivation of this resilient crop bears the promise of economic growth and stability. By harnessing the power of corn, countries can sow the seeds of economic prosperity, creating a ripple effect that permeates diverse sectors and stimulates development in rural and urban areas alike.
The Historical Significance of Maize in Agriculture

In the realm of agriculture, Maize has always played a fundamental and profound role. Through centuries of evolution, farmers have harnessed the potential of this versatile crop, shaping the foundations of civilizations and fostering economic prosperity. Maize, a plant of great adaptability and nutritional richness, has sustained communities, stimulated trade routes, and revolutionized farming practices, making it a cornerstone of agricultural history.
The advent of Maize cultivation marked a pivotal moment in agricultural development. Its cultivation brought about a transformation in human societies, enabling them to transition from nomadic hunter-gatherer lifestyles to settled agricultural communities. The innovative practice of growing Maize allowed ancient civilizations to establish permanent settlements, cultivate surplus food supplies, and develop economies based on agriculture. This shift from a subsistence-based existence to a food surplus-driven society paved the way for social advancement and the rise of complex civilizations.
As the cultivation of Maize spread across continents, it left an indelible mark on civilizations. In the Americas, Maize became synonymous with the ancient Mayans and Aztecs, who regarded it as a sacred crop intertwined with their religious and cultural practices. These civilizations exploited the versatility of Maize in various forms, utilizing it not only as a staple food source but also as currency, fuel, and even a means of preserving cultural heritage through art and architecture.
The influence of Maize stretched far beyond the Americas, impacting societies across the globe. In Europe, Maize introduced a new agricultural system known as the "Columbian Exchange" after Christopher Columbus's voyages. Maize, alongside other New World crops, was introduced to Europe, leading to enhanced food production, improved nutrition, and demographic shifts. European nations found Maize to be an adaptable and high-yielding crop, contributing to the growth of population centers and the development of agricultural infrastructure.
The historical significance of Maize cannot be understated, as it continues to shape agriculture in the modern world. Today, Maize remains one of the most widely grown and economically important crops, with its extensive use found in livestock feed, industrial products, and renewable energy production. The evolutionary journey of Maize stands as a testament to the ingenuity of humankind and the transformative power of agriculture.
The Versatility of Maize: Beyond Nutrition and Animal Feed
An exploration of the numerous applications of maize goes beyond its traditional role as a staple food and animal feed. This incredibly versatile crop offers a multitude of possibilities in various industries due to its unique characteristics and properties.
- Renewable Energy: Maize can be converted into biofuels such as ethanol, serving as a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. Its high starch content makes it an ideal feedstock for bioenergy production.
- Pharmaceuticals: Certain compounds derived from maize, such as zein protein, have potential applications in drug delivery systems and as biodegradable packaging materials.
- Industrial Uses: Maize starch can be utilized in the production of adhesives, coatings, and bioplastics, offering eco-friendly alternatives to petroleum-based products.
- Textiles: The fibers derived from maize husks and stalks can be transformed into textiles, offering a renewable and biodegradable option in the fashion industry.
- Construction Materials: Maize-based materials, such as panels and insulation, have shown promise as eco-friendly alternatives to traditional construction materials due to their renewable and insulating properties.
These examples merely scratch the surface of maize's versatility. The abundance of potential applications showcases the importance of exploring and maximizing the uses of this remarkable crop, opening new avenues for sustainable development in various industries.
Exploring the Nutritional Value of Maize Products

The section delves into the vast range of nutritional benefits offered by various maize products. By exploring the diverse array of essential nutrients and dietary components found in maize, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of its potential impact on human health and overall well-being.
Within this section, the focus will be on unveiling the nutritional value of an extensive selection of maize-derived products. Through meticulous examination, we aim to present a comprehensive overview of how these products can contribute to a well-balanced diet and offer potential health benefits.
From cornmeal to cornflour, corn oil to popcorn, this exploration aims to highlight the abundant nutritional content within these maize-based products. By detailing the presence of vitamins, minerals, dietary fiber, and various macronutrients, readers will gain valuable insights into the composition of these products.
Furthermore, the section will discuss the specific health benefits associated with the consumption of maize products. It will showcase how incorporating maize into one's diet can promote heart health, aid digestion, support weight management, and contribute to overall immune system functioning.
In conclusion, the nutritional value of maize products is often underestimated, overshadowed by their more common usage as staple foods. Through this section, readers will unearth the hidden potential and diverse range of nutrients offered by these maize products, fostering a greater understanding of their role in a healthy and balanced diet.
Revolutionizing Farming Techniques for Enhanced Corn Output
Farming practices have always played a crucial role in determining the success and productivity of crops. In recent years, the need to increase corn yield has become increasingly imperative. This section aims to explore innovative approaches that have the potential to revolutionize traditional farming methods, leading to a significant boost in corn production.
- Implementing Advanced Technology: Integrating cutting-edge technology, such as precision agriculture and remote sensing, can provide farmers with valuable insights into crop health, soil conditions, and water requirements. By utilizing data-driven decision-making, farmers can optimize the use of resources and make informed choices to enhance corn yield.
- Developing Sustainable Farming Techniques: Embracing sustainable farming practices, including crop rotation, cover cropping, and integrated pest management, can improve soil health, minimize the use of chemical inputs, and enhance natural pest control. By adopting a holistic approach, farmers can create a balanced ecosystem that supports robust corn growth and higher yields.
- Improving Seed Quality: Investing in research and development to develop genetically improved corn seeds can significantly impact corn yield. By focusing on traits such as disease resistance, drought tolerance, and high nutrient absorption, farmers can cultivate corn varieties that are more productive and better suited to their specific environments.
- Optimizing Nutrient Management: Applying precise and targeted fertilization techniques can optimize nutrient uptake by corn plants. Soil testing and analysis can help farmers tailor fertilizer application based on specific nutrient needs and soil characteristics. By ensuring an optimal balance of essential nutrients, farmers can maximize corn growth and yield.
- Deploying Precision Irrigation: Efficient water management is vital for corn cultivation. Implementing precision irrigation techniques, such as drip irrigation and soil moisture sensors, allows farmers to deliver water directly to plant roots, minimizing water waste and enhancing water-use efficiency. This approach not only conserves water resources but also improves corn growth and yield.
In conclusion, by embracing advanced technology, sustainable practices, improved seed quality, optimized nutrient management, and precision irrigation, farmers can revolutionize traditional farming techniques and achieve significant enhancements in corn yield. Implementing these approaches has the potential to pave the way for a more productive and sustainable future in corn cultivation.
The Promise of Corn-Based Biofuels in Sustainable Energy Generation
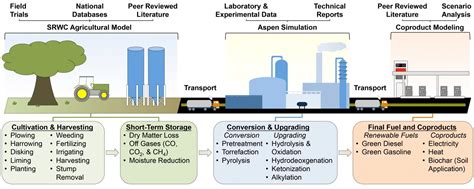
The extensive research and development being conducted in the realm of biofuels has brought attention to the immense potential of corn-based alternatives in facilitating sustainable energy production. By harnessing the natural properties of corn, scientists are paving the way for a future where biofuels thrive as a viable and environmentally friendly option. This section explores the various aspects and advantages of corn-based biofuels, shedding light on their ability to contribute to sustainable energy generation.
To comprehend the significance of corn-based biofuels, it is imperative to understand their renewable nature and compatibility with existing energy infrastructure. Corn is a versatile crop that can be easily grown and harvested, making it readily available as a renewable resource. Moreover, the established agricultural practices surrounding corn cultivation can seamlessly integrate with current farming techniques, minimizing the need for extensive modifications. This inherent compatibility makes corn-based biofuels a practical and viable option in the broader context of sustainable energy production.
One of the key advantages of corn-based biofuels lies in their potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. As the world grapples with the challenges posed by climate change, the importance of transitioning to greener and cleaner energy sources becomes increasingly evident. Corn-based biofuels offer a tangible solution by releasing significantly lower levels of carbon dioxide when compared to traditional fossil fuels. This reduction in emissions presents an opportunity to mitigate environmental harm while simultaneously addressing the growing demand for energy.
| Advantages of Corn-Based Biofuels |
|---|
| 1. Renewable resource |
| 2. Compatibility with existing farming techniques |
| 3. Reduced greenhouse gas emissions |
| 4. Potential for economic growth in the agricultural sector |
| 5. Enhancing energy independence and security |
Furthermore, corn-based biofuels offer the potential for economic growth in the agricultural sector. Expanded production of corn for biofuel purposes can open up new avenues for farmers, helping to stimulate rural economies and create employment opportunities. This economic synergy, coupled with the environmental benefits, lays a strong foundation for the viability and sustainability of corn-based biofuels.
Lastly, the utilization of corn-based biofuels contributes to enhancing energy independence and security. By reducing reliance on fossil fuels, which are often sourced from unstable regions, countries can bolster their energy autonomy. This reduction in dependence on foreign oil not only improves national security but also creates a more stable energy landscape for future generations.
In conclusion, the potential of corn-based biofuels in sustainable energy production is a game-changer worth exploring. With its renewable nature, reduced emissions, economic benefits, and contribution to energy independence, corn-based biofuels present an attractive solution to propel the world towards a greener and more sustainable future.
Preservation of Genetic Variety in Maize for Future Generations
In the quest to secure a thriving future for maize, it is crucial to understand the significance of preserving genetic diversity within this remarkable crop. This section delves into the imperative task of safeguarding the varied genetic makeup of maize, ensuring its resilience and adaptability for generations to come.
The Essence of Genetic Diversity
Genetic diversity refers to the multitude of unique traits and characteristics found within a particular species. In the case of maize, genetic diversity manifests itself through an array of variations in traits such as color, taste, pest resistance, and yield potential. This diversity acts as a natural shield against environmental challenges, providing a pool of genes that can be tapped into to enhance the crop's resilience in the face of changing climates, emerging pests, and diseases.
The Threat to Genetic Diversity
Unfortunately, the cultivation of commercial corn varieties has led to a considerable reduction in genetic diversity. The emphasis on a handful of high-yielding hybrids has resulted in the neglect of many landraces and heirloom varieties that possess unique genetic traits. This homogenization not only endangers the potential for future innovation and adaptability but also puts the overall maize ecosystem at risk. Losses in genetic diversity can lead to increased vulnerability to pests, diseases, and environmental stressors, making preservation efforts crucial for sustaining the crop's long-term viability.
Preservation Initiatives
Several initiatives and organizations have intervened to address the need for preserving genetic diversity in maize. These efforts involve the active collection, conservation, and cataloging of diverse germplasm, which encapsulates the range of genetic material present within maize. Gene banks and seed vaults serve as repositories for storing a vast array of maize samples, ensuring their availability for future research and breeding endeavors. Additionally, collaborations between farmers, scientists, and conservationists are underway to facilitate the on-farm conservation of landraces and heirloom varieties, ensuring their continued cultivation and preservation of their unique genetic traits.
The Importance of Future Access
Efforts towards preserving genetic diversity in maize serve not only present needs but also future generations. By safeguarding the genetic heritage of maize, we empower scientists, breeders, and farmers to unlock the potential for developing improved varieties that can provide sustainable solutions to hunger, malnutrition, and environmental challenges. Embracing the value of genetic diversity in maize is a testament to our commitment to fostering agricultural innovation, food security, and the well-being of our planet.
Navigating Challenges: Dealing with Pests, Diseases, and the Impact of Climate Change in Corn Farming

In the realm of corn cultivation, various obstacles arise that challenge the growth and prosperity of this staple crop. This section delves into the perils posed by pests, the threat of diseases, and the ever-evolving dilemma of climate change. Discover how farmers grapple with these hurdles and find innovative solutions to ensure the sustainability of corn farming.
Pest Management:
Pests have long plagued corn farmers, leading to significant yield losses and economic setbacks. In this segment, we explore the diverse array of pests that target corn crops, from insects like corn borers and armyworms to rodents and birds. Discover the impact of these pests on the growth and development of corn plants and the ingenious techniques employed by farmers to mitigate their effects. Learn about integrated pest management strategies and the use of biological control agents to maintain a balanced ecosystem in corn fields.
Combatting Diseases:
Diseases can wreak havoc on corn crops, jeopardizing not only the yield but also the quality of the harvest. This segment unravels the various fungal, bacterial, and viral diseases that pose a threat to corn cultivation. From common afflictions like leaf blight and rust to more destructive pathogens like corn smut and stalk rot, we delve into the symptoms, transmission methods, and preventive measures employed by farmers to protect their crops. Explore the role of crop rotation, seed treatments, and disease-resistant corn varieties in curbing the spread of diseases and preserving the health of corn plants.
The Impact of Climate Change:
Climate change presents an urgent and complex challenge for corn farmers. This section examines the multifaceted effects of climate change on corn cultivation, such as shifts in temperature, precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events. Delve into the repercussions of these changes on the growth cycle, water requirements, and overall productivity of corn plants. Discover the innovative adaptations and mitigation strategies adopted by farmers, including the adoption of drought-tolerant varieties, precision irrigation techniques, and sustainable farming practices to minimize the impact of climate change on corn crops.
By understanding the intricacies of pest management, disease control, and climate change adaptation, we can foster resilience in corn farming and pave the way for a future where this vital crop can thrive despite the challenges it faces.
Exploring Opportunities and Economic Advantages of Investing in Maize Production
Within the realm of corn cultivation lies a world of untapped possibilities, waiting to be harnessed for economic prosperity. This section delves into the myriad of opportunities and economic benefits that arise from investing in the production of maize, showcasing its potential as a lucrative and sustainable venture.
One of the key advantages of investing in maize production is the ever-increasing demand for this versatile crop. With its abundant applications in multiple industries, ranging from food and feed to biofuel and industrial manufacturing, maize presents a consistent and reliable market. The diversified uses of maize create a wide array of revenue streams, making it an attractive option for investors seeking both stability and growth.
Furthermore, the geographical adaptability of maize cultivation is another noteworthy factor that enhances its economic potential. Maize can be grown in various climates and soil types, allowing for flexible and scalable production across different regions. This adaptability not only mitigates the risks associated with volatile weather conditions but also opens up possibilities for investment in areas where agricultural resources and infrastructure may be underutilized.
Investing in maize production also presents a unique opportunity to contribute to rural development. The crop's labor-intensive nature fosters job creation, particularly in areas with high unemployment rates. By investing in maize cultivation, investors can actively promote social and economic progress in rural communities, fostering prosperity and reducing poverty levels.
In addition to its economic advantages, investing in maize production aligns with environmental sustainability efforts. Maize can be cultivated through advanced farming techniques such as precision agriculture and conservation agriculture, which contribute to resource conservation and minimize the negative environmental impact. By investing in maize production, investors can actively participate in sustainable agricultural practices and support the shift towards a greener and more resilient future.
In conclusion, the opportunities and economic benefits of investing in maize production are vast and promising. From the versatile market demand to its adaptability, contribution to rural development, and alignment with sustainability goals, maize cultivation proves to be an attractive investment prospect. As the world continues to evolve, embracing the potential of maize cultivation is a strategic decision that encompasses both financial gains and positive societal impact.
FAQ
What are some benefits of corn cultivation?
Corn cultivation offers various benefits such as providing staple food, animal feed, raw material for biofuel production, and employment opportunities in the agricultural sector.
What challenges are faced in corn cultivation?
Some challenges in corn cultivation include pests and diseases affecting crop yield, soil erosion, climate change impact, and market fluctuations affecting profitability.
How can farmers maximize corn cultivation potential?
Farmers can maximize corn cultivation potential by adopting modern farming techniques, using high-yield corn varieties, practicing efficient irrigation, implementing integrated pest management, and staying updated with market trends.
Is corn cultivation environmentally sustainable?
Corn cultivation can be environmentally sustainable if proper agricultural practices are followed, such as soil conservation, minimal use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, and the promotion of crop rotation to maintain soil health.



