Within the patchwork of Africa's mesmerizing savannas, there exists a creature adorned in nature's most striking design. With their elegant black and white stripes, these magnificent animals effortlessly capture our attention and ignite our curiosity. However, beyond their visually stunning appearance lies a multitude of enigmatic mysteries waiting to be unraveled. Embark on a journey into the heart of Zebra Kingdom, where secrets are whispered in the wind and tales of survival and unity enchant our souls.
Stripes - a universal symbol of a life well-lived and boundaries fiercely protected. The realm of zebras, however, stretches far beyond a mere pattern. Within their vast grassland territories, these captivating creatures navigate a delicate balance between camouflage and self-expression.
From their intricate social structures to their mysterious communication methods, zebras continue to bewilder scientists, researchers, and wildlife enthusiasts alike. As we delve deeper into their world, we come face-to-face with the peculiarities that make zebras the true enigmas of the animal kingdom. Journey with us as we explore the secrets of their distinctive stripes, the astonishing tales of kinship, and the unexpected connections that bind them to the savannah's delicate ecosystem. Strap on your safari hat and prepare for an immersive adventure into the captivating world of zebras.
The Enchanting Past and Evolution of Zebras
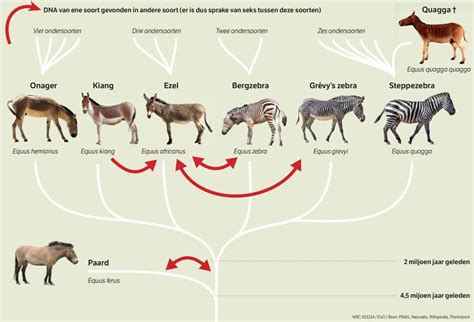
Behold the captivating journey of one of nature's most captivating creatures, as we delve into the intriguing history and evolutionary wonders of zebras. These magnificent beings have traversed through time, capturing the curiosity and awe of scholars and nature enthusiasts alike. From ancient tales to modern scientific discoveries, the story of zebras is a testament to the enduring allure of the natural world.
The origins of zebras can be traced back to the depths of prehistoric times, when the earliest equids roamed the grasslands and forests of ancient Africa. These ancient equids, with their distinctive striped coats and noble stature, have left an indelible mark on the evolutionary tapestry of the animal kingdom. Over the eons, zebras have evolved and adapted to thrive in diverse environments, showcasing an unparalleled resilience and survival instinct.
Ancient rock art and cave paintings have brought to light the longstanding fascination that zebras have evoked in human cultures throughout history. Their portrayal in art and folklore reflects not only their physical beauty but also the deep sense of mystery and enchantment that zebras inspire. From ancient Egyptians to African tribes, zebras have been revered as symbols of strength, freedom, and spiritual wisdom.
The enchantment of zebras extends beyond their captivating exterior. Scientific research has illuminated their pivotal role in shaping ecosystems and their unique adaptations that have allowed them to survive and flourish amidst diverse challenges. Their iconic black-and-white stripes, once thought to be purely ornamental, have now been discovered to play a crucial role in their survival, creating a natural camouflage and offering protection against predators.
Today, the legacy of zebras continues to fascinate and captivate. As we uncover the mysteries of their past and witness their thriving existence in the wild, we are reminded of the intricate web of life that binds us all. The study of their history and evolution serves as a testament to the resilience of nature and the relentless pursuit of adaptation and survival.
Understanding the Unique Adaptations of Striped Equines
Exploring the distinctive characteristics and evolutionary marvels of these black-and-white equine creatures is a fascinating endeavor. Zebras, with their mesmerizing striped patterns, possess a plethora of adaptations that allow them to thrive in their specific environments.
- Dazzling Camouflage: Zebras' bold stripes serve a variety of purposes, one of which is to confuse predators by creating an optical illusion that makes it difficult to single out an individual zebra from the herd. This adaptation provides them with a greater chance of evading predators and increases their chances of survival.
- Thermoregulation: The distinctive black-and-white stripes of zebras also play a crucial role in regulating their body temperature. The dark stripes absorb heat from the sun, while the lighter ones reflect it, creating air currents that help cool down their bodies in the scorching African savannah.
- Social Bonds and Communication: Zebras have a highly developed social structure, and their stripes contribute to effective communication within their herds. The unique stripe patterns of each zebra act as a sort of "identity card," allowing herd members to recognize each other and maintain strong social bonds.
- Biting Insect Protection: Another fascinating adaptation of zebras is their ability to repel biting insects such as horse flies and tsetse flies. The striped coat of zebras repels these pests by disorienting them, making it difficult for them to land and bite. This adaptation helps zebras minimize the risk of disease transmission and ensures their overall well-being.
- Surviving in Harsh Environments: Zebras have evolved to survive in various environments, including areas with limited water sources. Their kidneys are highly efficient in conserving water, allowing them to thrive in arid regions by excreting highly concentrated urine and minimizing water loss through sweat.
These unique adaptations of zebras showcase their astounding ability to adapt and succeed in their respective habitats. Understanding and appreciating these marvels of evolution is crucial for the conservation efforts aimed at preserving the marvelous creatures and ensuring their future survival.
The Social Dynamics and Communication among Zebra Herds

Zebras, enchanting creatures of the savannah, possess a complex social structure and fascinating communication methods that facilitate their daily interactions and ensure the harmony of their herds.
Within zebra herds, social dynamics play a crucial role in maintaining order and fostering successful collective endeavors. These herbivorous mammals exhibit an intricate system of hierarchy, where dominant individuals hold control over resources and access to mates. Strong bonds and complex relationships are formed within the herd, resulting in a structured society that promotes cooperation and unity.
Communication among zebras takes place through a variety of visual and auditory cues. Physical gestures, such as ear movements and body postures, are employed to convey messages of dominance, submission, or warning. Subtle changes in these expressions can signal shifts in social dynamics or impending threats within the group.
Vocalizations also play a significant role in zebra communication. Equipped with a repertoire of distinct vocal calls, zebras can convey specific messages to their counterparts. The iconic braying sounds, akin to a horse's neigh, can be heard during greetings, territorial disputes, or when individuals are separated from their group. These vocalizations serve as a means of identifying one another and maintaining coherence within the herd.
Visual displays further enhance communication among zebras. Their unique black and white striped coat patterns serve as individual identifiers, enabling herd members to recognize one another from afar. Additionally, these striking patterns likely play a role in confusing predators, making it harder for them to single out one zebra within a group. The stripes serve as a visual representation of a unified front, a symbol of the collective strength of the herd.
In conclusion, the social dynamics and communication among zebras are essential components of their lives. From establishing hierarchical structures to utilizing visual displays and vocalizations, zebras have evolved a remarkable system to foster cohesion and cooperation within their herds. Understanding these complexities is key to unraveling the mysteries of these captivating and captivating creatures of the savannah.
Unlocking the Mystery of Zebra Stripes: Theories and Explanations
The enigmatic patterns adorning the graceful bodies of zebras have intrigued scientists and researchers for centuries. In this section, we delve into the captivating realm of zebra stripes to unravel the secrets behind their existence, exploring various theories and explanations that have been put forth by experts in the field.
Camouflage Hypothesis:
One prominent theory suggests that the unique black-and-white stripes of zebras serve as a form of camouflage in their natural habitats. These mesmerizing patterns disrupt the outlines of their bodies, making it difficult for predators to accurately estimate their distance, direction, and overall presence. By blending into their surroundings, zebras gain a significant advantage in evading potential threats, highlighting the remarkable adaptation strategies of these remarkable creatures.
Thermoregulation Theory:
Another intriguing hypothesis proposes that the zebra stripes act as a mechanism to regulate body temperature. The alternating black and white stripes create air currents when sunlight filters through them, generating small variations in temperature. This thermal difference may aid zebras in keeping cool amidst hot African savannahs or warm during chilly nights, offering a distinctive advantage in the harsh and ever-changing climatic conditions they inhabit.
Social and Defensive Role:
Beyond practical functionality, some researchers contend that zebra stripes play a significant role in social interactions and defense mechanisms. These stunning patterns are believed to assist in visually distinguishing individuals within a herd, aiding in bonding and recognition. Additionally, they may create an optical illusion, making it difficult for predators to single out a particular zebra from a group, enhancing overall herd safety.
Insect Repellent Hypothesis:
An unconventional theory proposes that zebra stripes serve as a natural defense against irritating insects, such as flies and mosquitoes. It is claimed that the striped pattern interferes with insect vision, making it harder for them to land on the zebra's body, thus reducing the risk of bites or disease transmission. This peculiar hypothesis adds yet another layer of complexity to the multifaceted nature of zebra stripes.
Through exploring these diverse theories and explanations, we begin to unravel the marvels of zebra stripes, shedding light on the astonishing adaptations and evolutionary mysteries that make zebras one of the most captivating creatures in the animal kingdom.
The Ecological Significance of Zebras in Their Habitat

Zebras play a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of their ecosystem, showcasing remarkable adaptability and unique behavioral patterns. Their presence influences and shapes various ecological processes, making them an indispensable component of their habitat.
1. Key Herbivores:
Zebras, as herbivores, contribute significantly to their ecosystem by consuming vast quantities of grasses, leaves, and other vegetation. This grazing behavior not only controls the growth of plants but also promotes biodiversity by enabling the survival of species that depend on open grasslands. Their selective feeding habits also play a crucial role in shaping plant communities by influencing the abundance and distribution of different plant species.
2. Seed Dispersers:
Zebras act as crucial seed dispersers, as they often consume fruits and seeds along with their grazing activities. Through these feeding habits, zebras help disperse seeds over vast distances, facilitating the colonizatiin of new areas by plant species. This process plays a vital role in ensuring the survival and expansion of vegetation, making zebras indispensable for maintaining healthy ecosystems.
3. Prey for Predators:
Zebras, with their distinctive black and white striped appearance, have evolved as a survival strategy against predators such as lions, hyenas, and cheetahs. Their strong herding instincts and alert behavior allow them to quickly detect and evade potential threats. The presence of zebras in an ecosystem provides a critical source of prey for these carnivores, playing a crucial role in regulating predator populations and maintaining the delicate balance of predator-prey dynamics.
4. Soil Fertilization:
Zebras contribute to soil fertilization through their grazing and digestive processes. Their digestive systems break down plant material, releasing valuable nutrients into the soil. Moreover, their droppings act as a natural fertilizer, enriching the soil with essential nutrients that support the growth of various plant species. This nutrient cycling process ensures the overall health and productivity of the ecosystem.
5. Indicator Species:
Due to their specific habitat requirements, zebras serve as indicator species for the overall health and condition of the ecosystem they inhabit. Any significant changes in their population size, distribution, or behavior can indicate disturbances or imbalances in the ecosystem. Monitoring and studying zebras allows scientists to gain valuable insights into the overall well-being of their habitat and make informed conservation decisions.
In conclusion, zebras have a profound ecological impact on their environment. As herbivores, seed dispersers, prey for predators, contributors to soil fertilization, and indicator species, they contribute to the overall health and functioning of their ecosystem. Understanding and protecting these magnificent animals is crucial for ensuring the preservation of their habitat and the numerous benefits they bring to their ecosystem.
Threats and Conservation Efforts: Ensuring the Survival of Zebras
As we delve into the world of these remarkable creatures, it is imperative to address the challenges and risks that threaten the existence of zebras. It is through focused conservation efforts and an understanding of these threats that we can contribute to the survival of these magnificent animals for future generations.
- Habitat Loss: One of the primary threats faced by zebras is the loss of their natural habitat. With expanding human populations and increased urbanization, the shrinking grasslands and woodlands leave zebras with limited areas to roam and find food.
- Poaching: Conservationists are combating illegal poaching, which targets zebras for their skins and meat. The demand for zebra products in certain regions poses a significant risk to the species' survival and must be addressed through stringent law enforcement and education.
- Climate Change: As global temperatures rise and weather patterns shift, zebras face the challenge of adapting to these changes. Droughts and unpredictable rainfall can result in the scarcity of food and water resources, putting additional strain on zebras.
- Invasive Species: The introduction of non-native plant species can disrupt the intricate balance of ecosystems that zebras depend on. Invasive species can outcompete native vegetation, leading to reduced food availability for zebras and other wildlife.
Despite these threats, significant conservation efforts have been undertaken to safeguard zebras and their habitats:
- Protected Areas: The establishment of protected areas, such as national parks and reserves, provides crucial refuge for zebras, allowing them to live undisturbed and maintain their natural behaviors.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in conservation initiatives is vital for creating sustainable solutions. Through education, alternative livelihood opportunities, and the promotion of eco-tourism, communities can become proactive partners in zebra conservation.
- Scientific Research: Ongoing scientific studies help deepen our understanding of zebra behavior, migration patterns, and genetic diversity. This knowledge empowers conservationists to develop targeted strategies for the preservation of zebras.
- International Cooperation: Collaborative efforts among governments, organizations, and individuals on a global scale are essential for effective zebra conservation. Sharing best practices, supporting anti-poaching efforts, and raising awareness play a vital role in ensuring the survival of zebras.
By addressing the threats faced by zebras and implementing comprehensive conservation measures, we can secure a future where these awe-inspiring animals continue to roam freely, enriching our world with their presence.
FAQ
What are some interesting facts about zebras?
Zebras are fascinating creatures that possess several intriguing qualities. Firstly, their black and white stripes serve as a natural defense mechanism against predators. These stripes also help to regulate their body temperature in hot weather. Zebras are herbivores and feed on grass, leaves, and bark. They are highly social animals and live in herds, known as 'harems.' Additionally, zebras communicate through various sounds and body language. Overall, zebras are truly magnificent animals!
Where do zebras primarily live?
Zebras are native to the grasslands and savannas of Africa. They can be found in various countries such as Kenya, Tanzania, South Africa, and Botswana. These regions provide the zebras with the habitat they require, rich in grass and water sources. Some zebras also migrate in search of food and water, adapting to different environmental conditions.
How do zebras defend themselves against predators?
Zebras have evolved several mechanisms to protect themselves from predators. Their most notable defense is their unique black and white striped coat, which confuses and deters predators such as lions and hyenas. The stripes create an optical illusion, making it difficult for predators to gauge the speed and movement of the zebra. Zebras also have powerful hind legs that they use to kick attackers if threatened. Additionally, they live in herds, which increases their overall safety as predators are often reluctant to attack a large group.
What is the lifespan of a zebra?
The lifespan of a zebra can vary depending on various factors, including the species and the environment it lives in. On average, zebras can live up to 25 years in the wild. However, in captivity, where they receive proper care and nutrition, zebras can live even longer, sometimes reaching up to 40 years of age. It is important to note that factors such as predation, disease, and availability of resources can affect the lifespan of zebras in the wild.
Are zebras endangered?
Currently, most species of zebras are not considered endangered. However, the Grevy's zebra is listed as endangered on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. The Grevy's zebra faces multiple threats, including habitat loss, competition for resources with livestock, and hunting. Conservation efforts are being implemented to protect this species and ensure its survival. It is crucial to raise awareness about the importance of preserving zebras and their habitats to prevent any future endangerment.



