The human body often holds secrets that unravel through dreams, being presented like enigmatic riddles waiting to be deciphered. These nocturnal visions, characterized by their thought-provoking nature, can sometimes delve into the realm of medical conditions that affect our lungs - those crucial organs enabling us to draw breath and embrace life's wonders.
Within the intricate fabric of human existence, where the harmony of health is a cherished goal, respiratory disorders can emerge like inconspicuous whispers amidst the cacophony of existence. This ethereal symphony of affliction encompasses a multitude of circumstances that can upset the delicate balance within our bodies, leading to an array of disconcerting indications.
With bated breath, we embark on a journey to uncover the web of origins that entangles respiratory ailments. Exploring the labyrinthine corridors of potential triggers, synonymous with the intricacies of causation, we strive to illuminate the path towards understanding. Adorned with the knowledge of why and how these conditions manifest, we empower ourselves to challenge their stronghold on our well-being.
Guided by the light of awareness, we recognize the significance of recognizing the symptoms that may signal the presence of respiratory distress. From the subtlest nuances that tickle our lungs and beckon us to take notice, to the unmistakable sirens that blare with unwavering urgency, indications manifest themselves in various ways. The body, ever the messenger, seeks to communicate through the language of discomfort, urging us to take heed and seek solace in the arms of care, where healing is possible.
Contributing Factors to Respiratory Conditions
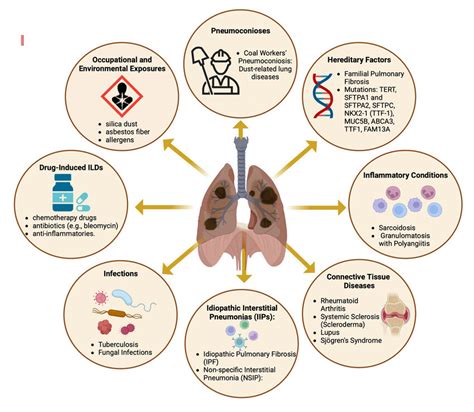
There are several underlying elements that can lead to the development of respiratory conditions. These factors can range from environmental influences to personal habits and genetic predispositions. Understanding the causes of lung disease is essential for prevention, early detection, and effective treatment.
1. Environmental Exposure:
- Prolonged exposure to air pollution, such as industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, and tobacco smoke, can significantly increase the risk of developing lung diseases.
- Inhalation of irritants or harmful substances like asbestos, silica dust, or chemical fumes can also damage the delicate lung tissues over time.
- Living or working in environments with poor ventilation or high levels of indoor pollutants, such as mold, radon, or secondhand smoke, can contribute to the development of respiratory conditions.
2. Occupational Hazards:
- Some jobs involve exposure to hazardous substances, such as coal dust, asbestos, or silica, which can lead to the development of occupational lung diseases.
- Workers in industries like construction, mining, agriculture, or manufacturing may face a higher risk due to the nature of their work.
3. Genetic Factors:
- Certain lung diseases have a hereditary component, meaning individuals may be more prone to developing them if they have a family history of the condition.
- Genetic mutations or abnormalities can affect the respiratory system's functioning or make individuals more susceptible to infections or inflammations.
4. Chronic Respiratory Infections:
- Recurrent infections, such as pneumonia, bronchitis, or tuberculosis, can weaken the lungs and compromise their ability to function properly, potentially leading to chronic lung diseases.
- Poor management of these infections or inadequate treatment can result in long-term damage to the respiratory system.
5. Lifestyle Choices:
- Certain lifestyle choices, including smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke, significantly increase the risk of developing lung diseases like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or lung cancer.
- Inadequate nutrition, sedentary lifestyle, or lack of regular exercise can also weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to respiratory conditions.
By understanding the various causes of lung disease, individuals can take proactive measures to reduce their risk of developing these conditions. It is essential to create a healthy environment, avoid harmful exposures, undergo regular check-ups, and adopt a lifestyle that promotes respiratory health.
Unveiling the Underlying Factors Contributing to the Onset of Respiratory Conditions
Delving into a comprehensive exploration of the intricate web of determinants that influence the emergence of respiratory disorders, this section aims to unveil the multidimensional aspects behind the development of lung diseases. By examining the underlying factors with precision and insight, a deeper understanding of the causes and triggers can be achieved.
Symptoms of Respiratory Illness

When one's respiratory system is affected by a health condition, certain indications may arise that could serve as a warning sign. These symptoms can manifest in various ways and differ depending on the nature and severity of the illness. Recognizing and understanding these warning signs can help in identifying respiratory diseases and seeking appropriate medical attention.
1. Breathing Difficulties: One of the most common symptoms of respiratory illness is experiencing difficulty in breathing. This can be characterized by shortness of breath, wheezing, or a feeling of tightness in the chest. These sensations may range from mild to severe, severely impacting daily activities and overall quality of life.
2. Chronic Cough: A persistent cough that lasts for an extended period, typically more than eight weeks, can be a symptom of a lung disease. This cough may be accompanied by phlegm or blood, and may worsen over time. It is important to note that not all coughs are indicative of respiratory illnesses, as they can also be caused by other factors.
3. Chest Pain: Some individuals with respiratory illnesses may experience chest pain or discomfort. This can manifest as a sharp or dull pain in the chest area, and could be exacerbated by deep breathing or physical exertion. Chest pain can be a sign of various respiratory conditions and should be taken seriously.
4. Fatigue and Weakness: The respiratory system plays a vital role in delivering oxygen to the body's cells. When the lungs are affected by a disease, this can disrupt oxygen flow, resulting in fatigue and weakness. Individuals may experience a constant feeling of tiredness or lack of energy, hindering their ability to engage in normal activities.
5. Recurrent Infections: Respiratory diseases can weaken the immune system and make individuals more susceptible to frequent infections, such as pneumonia or bronchitis. These infections can be recurrent and may require intervention from healthcare professionals to prevent complications.
It is important to understand that the presence of these symptoms does not necessarily indicate the presence of a lung disease, as they can also be associated with other health conditions. However, if these symptoms persist or worsen over time, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Recognizing the Telltale Signs of Respiratory Problems
Identifying early warning signs of respiratory issues is crucial in preventing the development of more serious lung conditions. By carefully observing your body's signals and recognizing the subtle changes in your breathing patterns, you can take proactive steps to seek appropriate medical attention and prevent potential complications.
Here are some key indicators that may suggest the presence of respiratory problems:
- Shortness of breath: Feeling unable to catch your breath or experiencing difficulty breathing during daily activities that were previously effortless.
- Chronic cough: Consistently having a cough that lasts longer than three weeks, which may produce mucus or blood.
- Wheezing: A high-pitched whistling sound while breathing, often accompanied by a feeling of tightness in the chest.
- Chest pain: Discomfort or tightness in the chest area, which may worsen with deep breaths or coughing.
- Frequent respiratory infections: Repeated bouts of respiratory infections, such as bronchitis or pneumonia, may indicate an underlying respiratory issue.
- Unexplained weight loss: A noticeable and unintentional weight loss that occurs without changes in diet or exercise routine.
- Fatigue: Feeling consistently tired, even after adequate rest, due to the increased effort required for proper breathing.
If you are experiencing any of these warning signs, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and diagnosis. Remember, recognizing and addressing respiratory issues early on can greatly improve the effectiveness of treatment and ultimately lead to better long-term outcomes.
Treatment Options for Respiratory Conditions
For individuals experiencing respiratory conditions, there are various treatment options available to help alleviate symptoms and improve lung function. These treatment options aim to enhance quality of life and manage the progression of the condition, addressing specific needs and concerns of each individual.
- 1. Medications: Numerous medications are used to treat respiratory conditions, including bronchodilators to open up the airways, corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, and antibiotics to treat infections. The type and dosage of medication prescribed may vary depending on the specific condition and its severity.
- 2. Oxygen Therapy: In cases where the lungs are unable to provide sufficient oxygen to the body, oxygen therapy may be recommended. This involves the use of supplemental oxygen through nasal prongs, a mask, or a portable oxygen concentrator, helping to improve oxygen levels and reduce breathlessness.
- 3. Pulmonary Rehabilitation: Pulmonary rehabilitation programs involve a combination of exercise, education, and support to enhance lung capacity, increase physical fitness, and improve overall well-being. These programs often include tailored exercise routines, breathing techniques, and educational sessions on managing symptoms and reducing the risk of exacerbations.
- 4. Lifestyle Modifications: Certain lifestyle changes can greatly benefit individuals with respiratory conditions. This may include quitting smoking, avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke and other respiratory irritants, maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, and staying physically active within one's capabilities.
- 5. Respiratory Devices: Various respiratory devices are available to assist with breathing difficulties and improve lung function. These devices include inhalers, nebulizers, and airway clearance devices. Proper usage and regular maintenance of these devices are crucial for their effectiveness.
- 6. Surgical Interventions: In some cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to manage or treat certain respiratory conditions. Procedures such as lung transplantation, lung volume reduction surgery, or the removal of lung tumors may be recommended, depending on the specific condition and individual needs.
It is important to note that treatment options may vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the respiratory condition. Seeking guidance from healthcare professionals and specialists is paramount to determine the most appropriate treatment plan tailored to individual circumstances.
FAQ
What are the main causes of lung disease?
The main causes of lung disease can vary. Some common causes include smoking, exposure to pollutants or chemicals, infections such as pneumonia or tuberculosis, genetic factors, and long-term exposure to secondhand smoke. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the specific cause of lung disease.
What are the symptoms of lung disease?
The symptoms of lung disease can differ depending on the specific condition. However, common symptoms may include persistent cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, wheezing, coughing up blood, fatigue, and weight loss. It is important to note that these symptoms may not always indicate a serious lung disease, but it is recommended to seek medical advice if experiencing any of these symptoms.
What are the treatment options for lung disease?
The treatment options for lung disease will vary based on the specific condition and its severity. Some treatment options include medications to manage symptoms, oxygen therapy, pulmonary rehabilitation, lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, and in severe cases, lung transplantation. The best course of treatment will be determined by a healthcare professional after diagnosing the specific lung disease.



