In a world where individual autonomy is celebrated, it is essential to be aware of the potential hazards that lurk in the realm of intimate relationships. While venturing into the realm of romantic encounters, it is crucial to stay informed about the perils of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). These ailments, although often shrouded in secrecy and discomfort, deserve our attention and proactive efforts in safeguarding our physical well-being. Without intentionally contracting an STD, it is still valuable to understand the associated risks and learn how to safeguard ourselves against them.
While the topic of STDs may provoke unease, it is crucial not to bury our heads in the proverbial sand. Ignorance can only perpetuate the spread of these diseases and contribute to their societal impact. By acknowledging the complexities and delicacies surrounding this subject matter, we can begin to dismantle the stigma associated with STDs. This can be achieved through education, fostering open conversations, and promoting a culture of individual responsibility while maintaining compassion towards those affected.
This article aims to empower individuals who dare to explore their desires with the knowledge required to make informed decisions. Rather than succumbing to fear and avoiding intimate connections altogether, understanding the risks associated with contracting an STD arms us with the tools to protect ourselves. By examining the various types of STDs, exploring their transmission routes, and delving into prevention methods, we can navigate the labyrinth of sexual health with confidence and assertiveness.
Throughout this journey, we will learn about the unique characteristics and complexities of different STDs. Emphasizing the significance of maintaining open and honest communication with partners, we will explore practical strategies for protecting ourselves and minimizing the risks associated with intimate encounters. By embracing the power of knowledge, we can strike a balance between satisfying our desires and prioritizing our health. So, let us embark on this enlightening expedition, arm in arm, towards a safer and more fulfilling path of intimate exploration.
Dangers of Sexually Transmitted Infections

In this section, we will explore the various risks associated with the transmission of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and highlight the importance of protecting oneself from these potential dangers. It is crucial to have a clear understanding of the potential consequences of engaging in unprotected sexual activities, as well as the methods available to reduce the risks involved.
Health Hazards: Engaging in unprotected sexual activities can expose individuals to a variety of health hazards. STIs can cause serious and sometimes irreversible damage to the reproductive system, leading to infertility, pelvic inflammatory disease, and even an increased risk of certain types of cancer. Furthermore, certain STIs can significantly weaken the immune system, leaving individuals more susceptible to other infections and diseases.
Psychological Impact: Contracting an STI can also have a profound psychological impact on individuals. The stigma associated with STIs can lead to feelings of guilt, shame, and decreased self-esteem. These emotional repercussions can further contribute to a cycle of risky behavior and can negatively affect individuals' mental health and overall well-being.
Relationship Strain: Discovering that one has contracted an STI can put a strain on both romantic and sexual relationships. The disclosure of an STI can lead to trust issues, conflicts, and potential breakups. It is essential to communicate openly and honestly with partners about sexual health and to encourage regular testing and safe sex practices to maintain healthy relationships.
Prevention Strategies: Taking precautions and practicing safe sex can significantly reduce the risk of contracting STIs. This includes the consistent and correct use of barrier methods such as condoms, regular testing and screening, and limiting the number of sexual partners. It is important to stay informed about the latest prevention strategies and to prioritize sexual health in order to minimize the potential dangers associated with STIs.
In conclusion, understanding the dangers of contracting an STI is crucial for making informed decisions about sexual health. By recognizing the potential risks and taking proactive measures to protect oneself, individuals can reduce their vulnerability to STIs and maintain a healthy and fulfilling sexual life.
Understanding the Risks and Consequences
Recognizing the Dangers
It is crucial to comprehend the potential hazards and repercussions associated with engaging in risky sexual behavior. Develop your knowledge about the serious outcomes and long-term effects of acquiring sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), emphasizing both physical and emotional consequences. By having a comprehensive understanding of these risks, individuals can make informed decisions and take necessary precautions for their sexual health.
Awareness of Transmission
Stay informed about the various methods of STD transmission, empowering yourself to protect against exposure. Whether through sexual intercourse, sharing needles, or coming into contact with infected bodily fluids, understanding how STDs can be spread is essential for preventing their contraction. Explore the multiple routes of transmission and familiarize yourself with specific precautions to minimize the risks of exposure.
Health Risks for Different STDs
Not all STDs are created equal, and each poses unique health risks. Recognize that different sexually transmitted diseases carry distinct consequences, ranging from mild to severe. Understanding the specific health risks associated with each STD allows individuals to evaluate the potential impact on their well-being and take appropriate measures to protect themselves and their partners from harm.
Long-Term Consequences
Be aware of the potential long-term consequences that can arise from untreated or inadequately managed STDs. Some sexually transmitted diseases can lead to serious health complications, such as infertility, organ damage, or an increased risk of acquiring other infections, including HIV. Understanding these long-term consequences highlights the importance of early detection, proper treatment, and consistent prevention measures.
Protective Strategies
Now that you have gained an understanding of the risks and consequences associated with STDs, it is imperative to explore strategies for protection. Promote safe sexual practices, highlight the importance of regular testing, and discuss the effectiveness of barrier methods, vaccinations, and medication. By adopting these protective strategies, individuals can minimize their chances of acquiring an STD and safeguard their sexual health.
Exploring the Different Types of Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs)
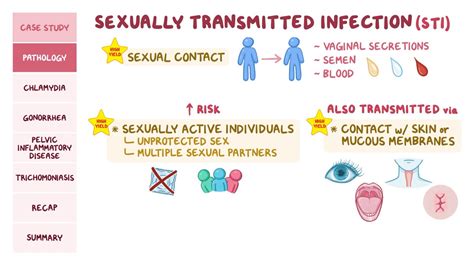
When it comes to sexual health, it is crucial to have a comprehensive understanding of the diverse array of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) that exist. These infections can be caused by various bacteria, parasites, and viruses, each presenting its own set of risks and potential complications. By familiarizing ourselves with the different types of STDs, we can become better equipped to protect ourselves and make informed decisions regarding our sexual health.
One of the most common types of STDs is chlamydia, a bacterial infection that affects both men and women. It can be transmitted through vaginal, anal, or oral sex, and often presents with no symptoms. Untreated chlamydia can lead to serious health issues such as infertility or pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
Gonorrhea, another prevalent STD, is also caused by a bacterial infection and can be transmitted through sexual contact. Like chlamydia, it can be asymptomatic in many cases, increasing the risk of unknowingly spreading the infection. If left untreated, gonorrhea can result in complications such as infertility or an increased susceptibility to HIV infection.
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a viral infection that is transmitted through skin-to-skin contact during sexual activity. With over 100 different strains, some types of HPV can cause genital warts, while others have been linked to certain types of cancer, including cervical, anal, and oropharyngeal cancer. Vaccines are available to help prevent HPV infection and reduce the risk of associated complications.
Herpes simplex viruses (HSV-1 and HSV-2) are responsible for genital herpes, a highly contagious infection that can be transmitted through sexual contact. It presents with painful sores or blisters and can periodically recur throughout a person's life, although antiviral medications can help manage symptoms and reduce the risk of transmission.
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is a viral infection that attacks the immune system, leaving the body vulnerable to various infections and diseases. It is primarily transmitted through unprotected sexual intercourse, sharing needles, and in some cases, from mother to child during childbirth or breastfeeding. While there is currently no cure for HIV, advancements in antiretroviral therapy (ART) have significantly improved the quality and lifespan of individuals living with the virus.
- Syphilis is a bacterial infection that can progress through different stages, each presenting its own symptoms and complications. It is typically transmitted through sexual contact but can also be passed from mother to child during pregnancy. Syphilis can cause severe health issues if left untreated and requires prompt medical attention.
- Hepatitis B and C are viral infections that primarily affect the liver. They can be transmitted through sexual contact, sharing needles, or from an infected mother to her child during childbirth. Chronic hepatitis infections can lead to liver scarring (cirrhosis), liver failure, or liver cancer.
- Trichomoniasis, caused by a parasite, is a common sexually transmitted infection that can affect both men and women. It often presents with symptoms such as itching, burning, or discharge from the genitals. While it can be easily treated with medications, it is important to seek prompt medical attention to prevent complications and reduce the risk of transmitting the infection to others.
By educating ourselves on the range of STDs that exist, we can actively take steps to protect our sexual health. Practicing safe sex, getting tested regularly, and engaging in open and honest conversations with our partners are all essential in prevention, early detection, and management of STDs.
Protecting Yourself: Methods of Prevention and Safe Practices
In order to maintain your sexual health and well-being, it is crucial to be aware of the various ways to protect yourself from sexually transmitted infections (STIs). By implementing effective prevention methods and practicing safe habits, you can significantly reduce the risk of contracting an STI. Here are some essential tips to consider:
- Condom Usage: Using condoms during sexual intercourse is one of the most effective ways to prevent the transmission of STIs. Ensure that you and your partner consistently and correctly use condoms throughout your sexual encounters.
- Regular Testing: Getting tested for STIs on a regular basis is vital, especially if you are sexually active. Regular testing helps identify any potential infections early on, allowing for timely treatment and preventing further transmission.
- Communication and Consent: Openly discussing sexual history, STI status, and sexual boundaries with your partner is crucial for informed decision-making and consent. Establishing clear communication can help minimize the risk of STI transmission.
- Vaccinations: Certain vaccines, such as the HPV vaccine, can protect against specific STIs. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine if you are eligible for any vaccinations.
- Reducing the Number of Partners: Limiting your number of sexual partners can significantly reduce the risk of contracting STIs. Engaging in monogamous relationships or reducing your sexual partners can decrease the likelihood of exposure.
- Practicing Mutual Monogamy: If both you and your partner have been tested and are STI-free, practicing mutual monogamy can be a safe option. Ensuring that neither partner engages in sexual activities outside of the relationship minimizes the chances of acquiring an STI.
- Using Dental Dams and Gloves: When engaging in oral or manual sexual activities, using dental dams or gloves can provide an additional barrier against STIs.
- Limiting Alcohol and Substance Use: Substance use, including excessive alcohol consumption, can impair judgment and lead to risky sexual behavior. Limiting alcohol and substance use can help you make safer choices.
By adopting these preventive measures and safe practices, you can take active steps towards protecting yourself from the risks associated with sexually transmitted infections. Remember, staying informed, communicating openly, and practicing safe sex are essential for maintaining your sexual health.



