In the depths of the vast aquatic realm, lies a world captivating in its enigmatic beauty. Here, within the vast expanse of the azure depths, exists a vision cherished by many, a dream of an expansive realm pulsating with an abundance of diverse marine creatures. This captivating vision, born from the depths of imagination, cultivates a longing within the hearts of those who yearn for a world where life thrives within the gentle embrace of the oceanic currents.
Imagine, if you will, a realm where the waters dance with an incredible array of vibrant and diverse organisms. From the graceful and majestic organisms that navigate the depths with ease to the seemingly inconspicuous yet essential creatures that form the very foundation of this underwater ecosystem, this oceanic utopia epitomizes harmonious coexistence. At its heart lies an intricate tapestry of interconnected life forms, each playing a pivotal role in sustaining the delicate balance that harmonizes within the vast expanse.
Envision a world where the placid depths come alive with a kaleidoscope of colors, where cerulean-hued waters are electrified by the vibrant pigments adorning the myriad of marine creatures. Ribbons of iridescent scales shimmer beneath the dappled sunlight, casting prisms of ethereal brilliance upon the tranquil depths. The whispering symphony of the currents becomes a veritable orchestra, as the marine inhabitants rhythmically sway in unison, exuding an otherworldly charm that captivates the minds of those lucky enough to witness this awe-inspiring spectacle.
Such a dream, a testament to the extraordinary wonders that lay beneath the surface, stirs a yearning within humanity. It fuels our desire to explore the enigmatic depths, to comprehend the intricacies of this harmonious kingdom, and to protect and cherish the invaluable resources that inhabit this oceanic paradise. With this dream of an ocean flourishing with an array of marine life, we are reminded of the magnificence of the natural world and the delicate balance that must be upheld to ensure its everlasting splendor.
The Decrease of Fish Populations in the Vast Depths
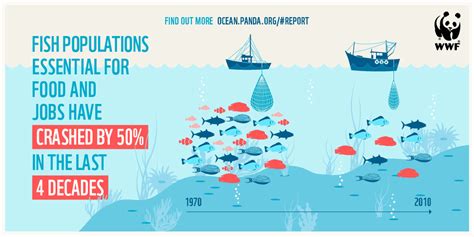
In the vast depths of the majestic aquatic realm, a disheartening trend has been observed – the gradual decline of once-thriving fish populations. The remarkable diversity and plenitude that once characterized these underwater ecosystems seem to be fading, giving rise to concern and prompting a need for urgent action. An intricate balance that took millions of years to evolve is now on the verge of rupture, as numerous factors converge to threaten the vitality of fish populations worldwide.
Overexploitation stands out as one of the primary forces behind the dwindling fish populations. As human societies continue to grow and expand, the demand for fish as a vital food source has reached unprecedented heights. With technological advancements enabling more efficient fishing practices, the delicate equilibrium between fishing and natural replenishment has been disrupted. As a result, fish stocks are unable to recover at the same rate they are harvested, leading to an alarming decline in their numbers.
Furthermore, the degradation of marine habitats exacerbates the challenges facing fish populations. Destructive activities such as bottom trawling and dynamite fishing indiscriminately damage coral reefs, seagrass meadows, and other crucial marine ecosystems. These habitats serve as breeding grounds, nurseries, and shelter for fish, and their loss directly impacts the ability of fish populations to thrive and sustain themselves.
Pollution emerges as another significant contributor to the declining fish populations. The relentless discharge of toxic substances, plastic waste, and oil spills contaminates the waters, infiltrating the food chain and impairing the reproductive capacity of fish. Not only do these pollutants pose a direct threat to fish health and survival, but they also disrupt the delicate balance of the entire marine ecosystem, leading to cascading effects that further exacerbate the decline of fish populations.
Climate change, with rising sea temperatures, ocean acidification, and altered currents, also looms large as an additional stressor on fish populations. These environmental shifts disrupt the intricate interplay between fish species and their habitats, causing changes in migration patterns, reproductive cycles, and overall species distribution. Consequently, the inability of fish to adapt quickly enough to these changing conditions further contributes to their declining populations.
The decline of fish populations in the vast depths of our oceans jeopardizes not only the ecological balance but also our own food security and livelihoods. Urgent action is required on a global scale to address these threats and ensure the long-term sustainability of our marine resources. By implementing effective conservation measures, sustainable fishing practices, and reducing pollution, we may yet restore the splendor of our oceans and revive the dreams of an ocean teeming with an abundance of fish.
The Impact of Overfishing and Climate Change
The increasing demand for seafood combined with the effects of climate change has led to significant repercussions on marine ecosystems. This section explores the consequences of overfishing and climate change on the fragile balance of our oceans, highlighting the importance of sustainable practices for the future of marine life.
Overfishing, or the excessive extraction of fish from aquatic environments, poses a grave threat to the biodiversity and overall health of marine ecosystems. This unsustainable practice disrupts the natural population dynamics, depleting fish stocks and destroying essential habitats. It not only affects the targeted species but also has cascading effects throughout the food web, impacting other organisms in the ecosystem.
Climate change, caused primarily by human activities such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, is another significant factor contributing to the depletion of fish populations. Rising sea temperatures, ocean acidification, and changing currents disrupt the delicate balance upon which marine life depends. These changes affect the distribution and abundance of fish species, pushing them to migrate to more suitable habitats or causing their populations to decline.
The combined consequences of overfishing and climate change are amplifying the vulnerability of marine ecosystems. Certain fish species, particularly those with slower reproductive rates or specific habitat requirements, are more susceptible to these impacts. This leads to imbalances in the ecosystem, affecting not only the fish stocks but also the communities that rely on them for food security and livelihoods.
Addressing the challenges of overfishing and climate change requires collective efforts from governments, fisheries management organizations, and the wider public. Implementing sustainable fishing practices, such as regulating fishing quotas, establishing marine protected areas, and promoting responsible consumption, can help restore and maintain the health of our oceans. Additionally, mitigating climate change through reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting renewable energy sources is crucial for the long-term sustainability of marine ecosystems.
| Key Points: | |
|---|---|
| 1. | Overfishing and climate change have detrimental effects on marine ecosystems. |
| 2. | Overfishing disrupts population dynamics and destroys habitats. |
| 3. | Climate change alters fish distribution and abundance. |
| 4. | Combined impacts amplify the vulnerability of marine ecosystems. |
| 5. | Sustainable fishing practices and climate change mitigation are essential for preserving marine life. |
The Significance of Sustainable Fishing Methods
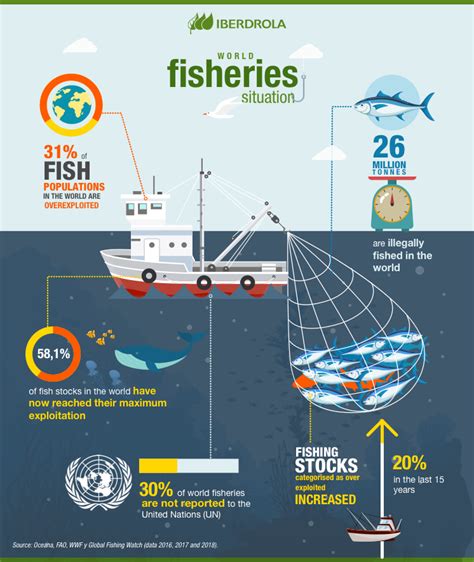
In the realm of aspirations, when visions encompass the vastness of the sea teaming with an abundance of aquatic creatures, it becomes imperative to acknowledge the crucial role of sustainable fishing practices. These practices, which prioritize the preservation and long-term viability of marine ecosystems, are of utmost importance in safeguarding the delicate equilibrium of underwater habitats and the continuity of aquatic life.
One of the key benefits of sustainable fishing is its ability to ensure the sustainability of fish populations. By adopting methods that avoid excessive fishing pressure, such as setting catch limits, implementing proper gear regulations, and monitoring fishing activities, we can strive to prevent the depletion of fish stocks. Through these measures, we endeavor to maintain a harmonious coexistence between humans and marine life, guaranteeing the availability of fish not only for present generations but also for future ones.
Furthermore, sustainable fishing practices go hand in hand with the concept of responsible consumption. By embracing methods that seek to minimize waste and bycatch, we can reduce the environmental impact of fishing activities. This entails employing selective fishing gear, which significantly reduces the unintentional capture of non-targeted species and ensures the survival and reproduction of untargeted marine organisms. By reducing wastage and optimizing resource utilization, we can contribute to the overall health of marine ecosystems and mitigate negative consequences on biodiversity.
Moreover, sustainable fishing practices support the long-term socio-economic well-being of coastal communities that heavily rely on fishing as a source of livelihood. By implementing sustainable fishing methods, we can foster the growth of local fish populations, ensuring a steady supply that benefits both artisanal and commercial fishers. Additionally, sustainable fishing practices can generate economic opportunities through eco-tourism, as healthier marine ecosystems attract visitors interested in witnessing the beauty and diversity of marine life.
In conclusion, the significance of sustainable fishing practices cannot be overstated. By safeguarding fish populations, minimizing environmental impact, and supporting the livelihoods of coastal communities, we can navigate towards a future where our dreams of an ocean teeming with life become a sustainable reality.
Preserving Marine Life for Future Generations
In this section, we will explore the crucial importance of conserving and safeguarding the diverse and plentiful underwater biodiversity that thrives in our vast and majestic bodies of water. By implementing responsible and sustainable fishing practices, we can ensure the long-term existence and viability of various aquatic species, allowing future generations to witness the beauty and abundance of marine life.
1. Adopting Sustainable Fishing Methods: It is vital to prioritize the adoption of sustainable fishing techniques that minimize the negative impact on marine ecosystems. This includes implementing measures such as selective fishing, where only specific target species are caught, reducing bycatch and avoiding the capture of non-target species. By utilizing fishing methods that align with ecological balance, we can help maintain healthy fish stocks and preserve the delicate marine food web.
2. Establishing Protected Marine Areas: Creating marine protected areas, or MPAs, is an effective approach to safeguarding and preserving vital habitats. These protected zones serve as sanctuaries for marine life, offering them a safe haven where they can reproduce, feed, and ensure the continuity of their survival. By designating specific areas for conservation, we can mitigate the adverse effects of overfishing, habitat destruction, and pollution on marine ecosystems.
3. Promoting Education and Awareness: Raising public awareness about the importance of preserving fish stocks and sustainable fishing practices is crucial for long-term success. Educational campaigns, workshops, and community outreach programs can play a significant role in informing individuals about the consequences of irresponsible fishing and ways to make a positive impact. By empowering communities with knowledge, we can foster a collective commitment to protect marine life and secure its future.
- 4. Encouraging Responsible Consumer Choices: Consumers can contribute to the preservation of fish stocks by making informed choices when purchasing seafood. Supporting sustainable fishing practices, such as buying fish that were caught using environmentally friendly methods, and opting for species that are not overexploited, can promote responsible fishing industry practices. Additionally, consumers can also opt for alternative protein sources, reducing the demand for fish and alleviating pressure on wild populations.
5. Collaborating with Fishing Communities and Stakeholders: Engaging with local fishing communities, industry stakeholders, and governments is crucial in the pursuit of effective fish stock preservation. By involving these key actors, we can develop policies and regulations that ensure sustainable fishing practices are promoted and enforced. Furthermore, empowering fishing communities with initiatives such as training programs and alternative livelihood opportunities can help transition towards more sustainable fishing practices.
In conclusion, the preservation of fish stocks for future generations is a collective responsibility. By adopting sustainable fishing methods, establishing protected marine areas, promoting education and awareness, encouraging responsible consumer choices, and collaborating with fishing communities and stakeholders, we can work towards ensuring the continued existence of diverse marine life in our oceans.
Restoring Fish Populations: Challenges and Solutions

Efforts to revive the dwindling numbers of aquatic creatures in our vast and bountiful marine habitats require a comprehensive understanding of the obstacles that impede their resurgence and the strategies essential for their revival.
In the quest to replenish marine fish populations, a multitude of challenges emerge, posing significant hurdles to achieving desired outcomes. These obstacles range from the depletion of natural habitats and the impacts of climate change to the overexploitation of fish stocks and the rampant pollution of our aquatic environments.
Addressing these challenges necessitates a multi-faceted approach that encompasses both short-term interventions and long-term conservation measures. The implementation of sustainable fishing practices, such as the establishment of catch limits and the adoption of selective fishing gear, is crucial to curbing overfishing and ensuring the survival and recovery of fish populations.
Furthermore, the restoration and protection of critical marine habitats, including coral reefs, seagrass meadows, and mangrove forests, play a pivotal role in supporting the resurgence of fish populations. These habitats serve as nurseries and breeding grounds for various fish species, providing essential food sources and shelter.
Collaborative efforts between governments, environmental organizations, and local communities are fundamental for the successful rebuilding of fish populations. Engaging stakeholders in sustainable management practices, promoting awareness and education, and implementing stringent regulations are vital steps towards safeguarding our oceans' biodiversity.
Ultimately, revitalizing fish populations requires a comprehensive and coordinated approach that combines scientific knowledge, policy interventions, and community participation. By embracing innovative solutions and prioritizing the protection of our marine ecosystems, we can safeguard the future abundance and diversity of fish in our seas.
The Role of Marine Protected Areas and Fishery Management
Ensuring the sustainability of marine ecosystems and maintaining healthy fish populations are crucial for the continued prosperity of our oceans. In this section, we will explore the significance and effectiveness of two essential strategies: marine protected areas and fishery management.
1. Marine Protected Areas (MPAs)
- Conservation zones
- Preservation of marine habitats
- Protection of biodiversity
- Safeguarding vulnerable species
- Fostering ecosystem resilience
Marine protected areas (MPAs) play a pivotal role in maintaining the delicate balance of coastal and marine ecosystems. These designated areas aim to protect and conserve critical marine habitats, while also promoting the sustainable use of marine resources. By establishing conservation zones, authorities can regulate human activities and minimize the negative impacts on marine biodiversity. MPAs provide sanctuary for fish species during crucial stages of their life cycles, enabling population growth and enhancing species resilience to external stressors. Moreover, these protected areas contribute to the overall health and productivity of surrounding marine environments, improving the well-being of fish communities and promoting ecological stability.
2. Fishery Management
- Monitoring fish stocks
- Sustainable fishing practices
- Quota systems
- Enforcement of regulations
- Collaborative governance
Effective fishery management is vital for maintaining the long-term viability of fish populations. Through the implementation of comprehensive strategies, such as monitoring fish stocks, setting catch limits, and applying sustainable fishing practices, it becomes possible to strike a balance between meeting human needs and safeguarding the marine environment. Quota systems help prevent overfishing and enable fish stocks to recover, ensuring their continuous availability for future generations. Furthermore, enforcing regulations and instituting collaborative governance frameworks involving scientists, policymakers, and stakeholders ensure that fishery management measures are effectively implemented and adapt to changing environmental conditions. By incorporating scientific research and embracing adaptive management approaches, fishery management contributes to the thriving marine ecosystems and supports sustainable fisheries worldwide.
In conclusion, the establishment of marine protected areas and the implementation of effective fishery management practices are essential for preserving the richness and diversity of marine life. Through their combined efforts, we can safeguard the future of our oceans, fostering an environment where fish populations can flourish and realizing the dreams of a thriving and abundant marine ecosystem.
FAQ
Why are fish populations declining in the ocean?
There are several reasons for the declining fish populations in the ocean. Overfishing, habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change are the main factors contributing to this decline. Overfishing involves catching fish at a faster rate than they can reproduce, leading to a depletion of their numbers. Habitat destruction, such as the destruction of coral reefs, deprives fish of their homes and food sources. Pollution, including the release of chemicals and plastics into the ocean, can also harm fish and their habitats. Additionally, climate change affects ocean ecosystems, making it difficult for fish to survive.
What are the consequences of fish population decline?
The consequences of fish population decline are widespread and significant. Firstly, it disrupts the balance of marine ecosystems. Fish play a crucial role in maintaining the health of these ecosystems by controlling the population of smaller organisms and providing food for larger predators. Their decline can lead to imbalances and cascading effects throughout the food chain. Moreover, fish provide a major source of protein and income for millions of people worldwide, especially in coastal communities. The decline of fish populations has severe economic implications for these communities, often leading to food insecurity and poverty. Additionally, the loss of fish species can have cultural and ecological impacts.
How can we restore fish populations in the ocean?
Restoring fish populations in the ocean requires a multi-faceted approach. One of the most important steps is implementing sustainable fishing practices. This involves setting catch limits, creating marine protected areas, and enforcing regulations to prevent overfishing. Habitat restoration is also essential, as it provides fish with suitable environments to reproduce and thrive. This can include initiatives to restore damaged coral reefs or create artificial reefs. Reducing pollution, particularly plastic pollution, is crucial for the health of fish populations and their habitats. Furthermore, addressing climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions can help preserve ocean ecosystems. International cooperation and collaboration between governments, scientists, and fishing communities are key to successful fish population restoration efforts.
What are the potential solutions to the overfishing problem?
There are several potential solutions to the overfishing problem. Firstly, implementing and enforcing fishing regulations is crucial. This can involve setting catch limits, establishing fishing seasons, and implementing size restrictions to allow fish to reach reproductive maturity. Creating marine protected areas where fishing is prohibited or restricted can also help fish populations recover. Another solution is promoting sustainable fishing practices, such as using selective fishing gear that minimizes bycatch. Encouraging aquaculture as an alternative to wild-caught fish can also help alleviate fishing pressure in the ocean. Additionally, consumer awareness and choosing sustainably harvested fish can drive market demand for responsible fishing practices.
How does climate change affect fish populations in the ocean?
Climate change has significant impacts on fish populations in the ocean. Rising sea temperatures, ocean acidification, and changes in currents and nutrient availability all affect fish in different ways. Some fish species may struggle to adapt to the changing conditions, leading to population declines. Changes in water temperature can disrupt the timing of fish spawning, affecting their reproductive success. Ocean acidification, caused by the absorption of carbon dioxide, can negatively impact the growth and survival of fish larvae and other marine organisms. Alterations in ocean currents and nutrient availability can also affect the distribution and abundance of fish species. Overall, climate change poses a major threat to the health and sustainability of fish populations in the ocean.
What is the article "Dreams of an Ocean Filled with an Abundance of Fish" about?
The article "Dreams of an Ocean Filled with an Abundance of Fish" discusses the optimistic view of a future ocean filled with a large population of fish. It explores the current decline in fish populations due to overfishing and the potential solutions to restore and maintain healthy fish populations.
Why are fish populations declining in the ocean?
Fish populations in the ocean are declining due to various factors, including overfishing, habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change. Overfishing, in particular, has led to the depletion of fish stocks and disrupted the balance of marine ecosystems.



