Indulging in the reverie of economical fuel costs has become an alluring pastime for many. An almost elusive notion that dances temptingly on the periphery of our collective consciousness, it beckons us with promises of financial relief and enhanced mobility. Yet, the pursuit of this ethereal chimera remains an ongoing endeavor, fraught with both anticipation and frustration.
Within the realm of everyday existence, the quest for accessible fuel prices has transcended its mere practical definition, morphing into a symbol of societal and economic stability. As individuals, we yearn for a reality where our hard-earned income stretches further, enabling us to explore new horizons and embrace life's opportunities without the shackles of exorbitant expenses.
Although one may be inclined to view these aspirations as mere flights of fancy or whimsical notions, they carry a profound significance that resonates deeply within the fabric of our daily lives. Fuel costs command a pivotal position in the economic landscape, impacting not only the lives of individuals but also the functionality and competitiveness of various industries.
With this in mind, it becomes imperative to dissect the underlying factors that contribute to the elusive nature of reasonably priced fuel. From geopolitical tensions to fluctuations in global oil production, an intricate web of influences intertwines to create a climate of uncertainty. Understanding these complexities can empower individuals to navigate the intricate paths towards attaining the illusion of affordable fuel prices.
Exploring the Factors Influencing Global Gasoline Prices
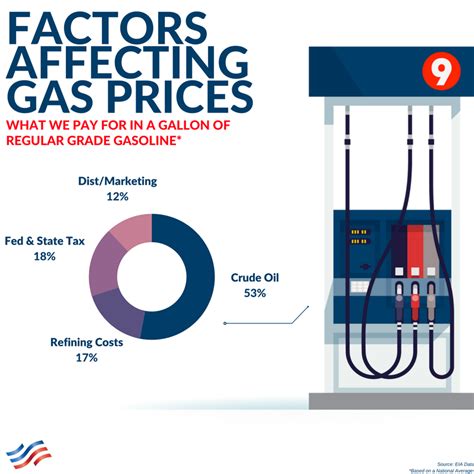
In this section, we will delve into the various elements that contribute to the fluctuations of gasoline prices around the world. Understanding these factors is crucial for comprehending the dynamics of fuel costs and their impact on consumers and economies.
First and foremost, geopolitical factors play a significant role in driving gasoline prices. Tensions in oil-producing regions, political unrest, and conflicts can disrupt the supply chain, leading to fluctuations in fuel prices. Additionally, international agreements and policies on production and distribution can also affect the cost of gasoline.
Economic conditions and market forces are also key factors. The supply and demand dynamics of oil, the primary raw material for gasoline, significantly influence its price. Factors such as global oil production, economic growth, and changes in consumer behavior all contribute to the volatility of gasoline prices.
Furthermore, the cost of refining and distributing gasoline can impact its final price. The expenses associated with refining crude oil into gasoline, transportation costs, and the efficiency of distribution networks all contribute to the variations in gasoline prices globally.
Last but not least, currency exchange rates influence fuel costs. Since oil is traded in US dollars, fluctuations in exchange rates can directly affect gas prices in countries with different currencies. A stronger local currency against the US dollar can result in more affordable gasoline prices for consumers, while a weaker currency can lead to higher costs.
By recognizing and understanding these various factors, policymakers, economists, and consumers can gain valuable insights into the intricate dynamics behind global gasoline prices. This knowledge can help shape strategies and policies to mitigate the impact of price fluctuations and work towards a more stable and sustainable energy future.
The Impact of Geopolitics on Gas Prices: Unpredictable and Unavoidable
In today's interconnected world, the prices of essential commodities such as fuel are influenced not only by economic factors but also by geopolitical events and relationships between nations. The intricate interplay of global politics can have a profound impact on gas prices, making them fluctuate in unpredictable ways, thus affecting individuals and businesses alike.
Geopolitical factors, which encompass political, diplomatic, and military affairs among nations, can create a ripple effect on gas prices. Tensions between major oil-producing countries or disruptions in supply routes can quickly drive prices up, leading to increased expenses for consumers. Conversely, diplomatic breakthroughs or stable relations between nations can alleviate such pressure, resulting in a more stable gas market.
The influence of geopolitics on gas prices is unavoidable due to the nature of international relations. Governments often employ various strategies and policies to safeguard their interests, which can directly or indirectly affect fuel costs. Embargoes, sanctions, or conflicts can disrupt oil production and transportation, leading to higher prices or even shortages. On the other hand, collaborations, trade agreements, or diplomatic engagements can foster stability and ensure a steady supply of gas, thus keeping prices manageable.
It is essential for individuals, businesses, and governments to stay informed and understand the dynamics of geopolitics to navigate the ever-changing gas market effectively. Awareness of potential geopolitical risks and developments can help make informed decisions regarding energy consumption, investment in alternative energy sources, or even long-term strategic planning.
In summary, the impact of geopolitics on gas prices is a reality that cannot be overlooked. The intricate relationships between nations, their policies, and conflicts shape the fuel market, making it unpredictable and unavoidable. Understanding these dynamics and staying informed is crucial for individuals and businesses to adapt and mitigate the effects of geopolitical events on gas prices.
Exploring Viable Alternatives to Gasoline: Beyond the Conventional Choices

When considering the question of viable alternatives to gasoline, it is essential to explore a range of options that extend beyond the conventional choices. In today's world, with increasing concerns about climate change and environmental impact, the need to find sustainable and efficient fuel sources has become more important than ever.
One potential alternative to gasoline is electric vehicles (EVs). These vehicles are powered by electricity, which can be obtained from renewable sources such as solar or wind energy. EVs offer a cleaner and greener option, reducing carbon emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. With advancements in technology, EVs are becoming more accessible and practical for everyday use.
Another option worth considering is hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs). These vehicles use hydrogen to generate electricity, producing only water vapor as a byproduct. FCVs offer the advantage of high energy density and quick refueling times, making them comparable to gasoline vehicles in terms of convenience. However, the infrastructure for hydrogen refueling is currently limited, which poses a challenge for widespread adoption.
Biofuels are another promising alternative to gasoline. Derived from organic matter such as crops or agricultural waste, biofuels can be used in existing vehicles without major modifications. Ethanol, a commonly used biofuel, can be mixed with gasoline to reduce emissions. Advanced biofuels, such as cellulosic ethanol or algae-based fuels, show potential for higher energy efficiency and lower environmental impact.
- Natural gas: Natural gas is a fossil fuel, but it releases fewer emissions compared to gasoline and diesel. Compressed natural gas (CNG) and liquefied natural gas (LNG) are used as alternative fuels in some vehicles and offer a cleaner burning option.
- Hybrid vehicles: Hybrid vehicles combine an internal combustion engine with an electric motor, offering improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. They can run on gasoline or switch to electric mode, making them a transitional option towards full electrification.
- Hydrogen gas: Hydrogen gas can be used directly as a fuel in internal combustion engines or through fuel cells to generate electricity. Although hydrogen production and infrastructure remain challenges, advancements are being made in this field.
- Public transportation and shared mobility: Encouraging the use of public transportation and shared mobility options such as carpooling can reduce the overall demand for gasoline-powered vehicles and promote more sustainable alternatives.
Exploring and investing in these viable alternatives to gasoline is crucial for a more sustainable and greener future. Each option has its own advantages and challenges, and further research and development are needed to overcome barriers and maximize their potential. By embracing these alternatives, we can reduce our dependence on gasoline and move towards a cleaner and more sustainable transportation system.
Saving Money at the Pump: Tips and Tricks for Reducing Fuel Costs
When it comes to the cost of fuel, many of us long for a way to decrease our expenses at the gas station. Fortunately, there are several techniques and strategies that can help us save money and reduce fuel costs. By implementing these tips and tricks, you can make a significant impact on your budget without compromising your transportation needs.
The Influence of Government Policies on Fuel Costs

In the realm of energy, governmental policies play a significant role in shaping the fluctuations of fuel expenses. With the power to implement regulations and introduce incentives, governments possess the ability to exert their influence on the price of fuel. By assessing market demands, supply and demand dynamics, and environmental considerations, policymakers have the means to affect the availability and affordability of transportation fuel for consumers.
Government policies may encompass a wide range of approaches, including taxation, subsidies, and regulations. Taxation policies can directly impact fuel costs by increasing or decreasing the amount of taxes levied on the production and consumption of fuel products. Subsidies, on the other hand, can provide financial support to various sectors of the industry, lowering production costs and ultimately influencing the market price of fuel. Additionally, regulations aimed at enhancing fuel efficiency standards, reducing emissions, or diversifying the energy mix can also contribute to changes in fuel prices.
Efforts to encourage the use of renewable energy sources can also impact the pricing of fossil fuels. Government support for alternative energy technologies, such as wind, solar, or biofuels, can shift the focus away from traditional hydrocarbon-based fuels and help mitigate the overall demand for fossil fuels, thereby contributing to fluctuations in their prices.
Furthermore, political stability in oil-producing countries can significantly influence fuel costs. Sanctions, conflicts, or geopolitical tensions that disrupt oil production or supply routes can lead to price spikes, making fuel more expensive for consumers. On the contrary, diplomatic negotiations or regional cooperation that ensure a stable flow of oil can help stabilize fuel costs and prevent sudden price surges.
In conclusion, government policies hold a considerable sway over the pricing of transportation fuel. By implementing taxation, subsidies, regulations, and supporting alternative energy sources, policymakers can shape the affordability and availability of fuel for consumers. Understanding the interplay between government policies and the energy sector is crucial for comprehending the factors that contribute to the ever-changing fuel prices.
Exploring the Viability of Renewable Energy Sources as a Potential Substitute for Gasoline
In the quest for a sustainable and eco-friendly future, the possibility of replacing gasoline with renewable energy sources has been a subject of great interest and ongoing research. This section explores the potential of harnessing alternative energy sources to potentially eliminate our dependence on traditional fossil fuels.
- Solar Power: With advancements in solar technology, harnessing the sun's energy has emerged as a promising alternative to gasoline. Solar panels are increasingly being used to power electric vehicles, providing an emission-free mode of transportation. Furthermore, solar energy can also be utilized to power industrial processes and other energy-intensive activities.
- Wind Energy: Wind turbines harness the power of wind to generate electricity, potentially offering an alternative to gasoline-powered engines. This renewable energy source has gained significant momentum in recent years, with large-scale wind farms being established worldwide. Wind energy can be particularly effective in coastal areas and regions with consistently strong wind patterns.
- Hydroelectric Power: Leveraging the force of flowing or falling water, hydroelectric power presents another avenue for replacing gasoline. Dams and turbines generate electricity from the kinetic energy of water, which can be used for various applications including transportation. However, the feasibility of implementing hydroelectric power is limited to areas with access to suitable water resources.
- Biofuels: Derived from organic matter such as crops, forestry byproducts, or algae, biofuels offer a renewable source of energy that can potentially replace gasoline. Biofuels can be used in vehicles without the need for engine modifications and are considered carbon-neutral since the CO2 emitted during combustion is offset by the CO2 absorbed during the growth of the organic matter used for their production.
While the potential of renewable energy sources as a substitute for gasoline is promising, it is essential to consider the challenges that accompany this transition. The efficiency, scalability, and cost-effectiveness of these alternative energy sources need to be continuously improved to ensure widespread adoption. Additionally, the development of appropriate infrastructure, such as charging stations for electric vehicles, must keep pace with the growing demand.
Ultimately, a comprehensive and diverse approach involving a combination of renewable energy sources, as well as advancements in technology and infrastructure, will be necessary to fully replace gasoline with sustainable alternatives. The pursuit of a future where renewable energy sources will fully replace gasoline requires continued research, innovation, and collaboration between government, industries, and individuals.
FAQ
Why are gas prices so high?
Gas prices are influenced by various factors such as global supply and demand, geopolitical events, and the cost of crude oil. When the supply of crude oil is limited or when there are conflicts in oil-producing regions, the price of gas tends to increase.
Are there any ways to get cheaper gas prices?
While it is not possible for individuals to directly control gas prices, there are several ways to potentially save money on fuel. These include shopping around for the cheapest gas stations, using fuel rewards programs, driving more fuel-efficient vehicles, and carpooling or using public transportation.
Will electric cars help bring down gas prices?
Electric cars have the potential to reduce gas prices in the long run. As more people switch to electric vehicles, there will be less demand for gasoline, which could lead to a decrease in gas prices. However, this transition will likely take time and there are currently infrastructure challenges that need to be addressed for widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
How do gas prices affect the economy?
Gas prices have a significant impact on the economy as they affect the cost of transportation. When gas prices are high, transportation costs increase for businesses, which can lead to higher prices for goods and services. Additionally, high gas prices can affect consumer spending and reduce disposable income, potentially slowing down economic growth.
What can the government do to lower gas prices?
The government can take several actions to potentially lower gas prices. These include negotiating with oil-producing countries for lower oil prices, implementing policies that promote energy independence and the use of alternative fuels, investing in public transportation and infrastructure, and regulating speculation in the oil market that can drive up prices.
Why are gas prices constantly rising?
Gas prices are determined by various factors, including global oil prices, supply and demand, and geopolitical factors. When global oil prices increase, it leads to higher gasoline costs at the pump. Additionally, conflicts or disruptions in oil-producing regions can impact the supply chain, causing prices to spike.
Is there any solution to control or reduce gas prices?
Controlling or reducing gas prices is a complex issue that depends on various factors. However, some possible solutions include investing in alternative fuel sources, incentivizing the use of electric vehicles, improving fuel efficiency in vehicles, and promoting public transportation systems. Government policies and regulations can also play a role in stabilizing gas prices.



