Within the intricate marvels of the oral realm lies a quagmire of enigmatic conundrums, one of which is veiled behind the veils of slumber - the visionary puzzle known to many as the nocturnal ravings of a burdened molar. As the mind seeks respite in the ethereal oasis of dreams, it often unwittingly grapples with the underlying grievances and complexities that afflict the dental dwellings within.
In these mystical realms of subconscious meanderings, the woeful plight of dental unrest unfurls its clandestine tendrils, bringing to light an array of deliberations and dissonance. The mind, in its infinite wisdom, employs this nocturnal stage to unravel the fragmented mysteries of oral afflictions, all while evading the use of explicit terminology. The repertoire of symptoms that accompany these nocturnal tales follow suit in their enigmatic guise, speaking volumes through symbolism and metaphor.
Engulfed in the labyrinthine realm of the mind's nocturnal wanderings, one must decipher the ethereal whispers and mystical reverberations that echo through the chambers of slumber. Through ardent introspection and a keen eye for the nuances of symbolism, the underlying causes of dental tumult can be painstakingly unearthed. Delve deep into the realms of this enigmatic landscape, as we unravel the secrets that lay dormant within the dreamscape of an ailing dental apparatus. Brace yourself for an odyssey of contemplation and enlightenment, as we embark on a journey to decode the silent language spoken by the subconscious facets of dentition.
The Basics of a Inflamed Dental Tissue
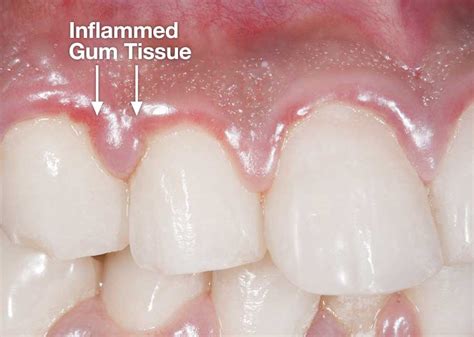
When dental tissue becomes inflamed, it can lead to a variety of uncomfortable symptoms and potential complications that require prompt attention. Understanding the fundamentals of an inflamed tooth can help individuals identify the signs early on, seek appropriate treatment, and prevent further dental issues.
Inflammation of dental tissue, also known as pulpitis, occurs when the soft inner part of the tooth becomes irritated and swollen. This condition can result from various factors, such as tooth decay, trauma, cracks or fractures in the tooth, or a failed dental procedure. The onset of pulpitis can bring about significant discomfort and should not be ignored.
Common symptoms of an inflamed tooth include persistent toothache, increased sensitivity to temperature extremes, swelling around the affected tooth, and a bad taste or odor in the mouth. Additionally, individuals may experience pain while chewing or biting down, as well as swollen lymph nodes in the neck or jaw. These indications should be evaluated by a dental professional to determine the most appropriate course of action.
Treating an inflamed tooth typically involves addressing the underlying cause of the inflammation and alleviating any associated discomfort. The recommended treatment may vary depending on the severity of the infection and the extent of damage to the tooth. In some cases, a root canal procedure may be necessary to remove the infected tissue and save the tooth, while in others, tooth extraction might be required.
| Common Causes of Dental Tissue Inflammation | Common Symptoms of an Inflamed Tooth |
|---|---|
| Tooth decay | Persistent toothache |
| Dental trauma | Increased sensitivity to temperature extremes |
| Cracks or fractures in the tooth | Swelling around the affected tooth |
| Failed dental procedures | Bad taste or odor in the mouth |
Understanding the Factors Behind Dental Infections
Introduction: This section aims to delve into the underlying causes and contributing factors that lead to dental infections, shedding light on the various triggers behind this oral health issue. By comprehending the determinants of tooth infections, individuals can adopt preventive measures and seek timely treatment, ultimately safeguarding their dental well-being.
Microorganisms and Bacterial Invasion: Dental infections are predominantly the result of the intrusion of harmful microorganisms into the teeth and surrounding tissues. Bacteria, which commonly reside in the oral cavity, can exploit vulnerable areas, such as cavities or cracks, and establish an infection. These microorganisms thrive in the presence of plaque buildup, which highlights the importance of maintaining good oral hygiene practices.
Untreated Dental Issues: Another prominent cause of tooth infections is the neglect or delay in addressing dental problems promptly. Conditions like tooth decay, gum disease, or cracked teeth can create openings for bacteria to infiltrate and cause infection. Therefore, it is crucial to address and treat any dental issues promptly to prevent the development of more severe complications.
Compromised Immune System: Individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those with certain medical conditions or undergoing immunosuppressive therapies, are more susceptible to dental infections. A weakened immune response hampers the body's ability to fight off bacteria, increasing the risk of infection. Recognizing this vulnerability is essential in managing oral health effectively for individuals with compromised immunity.
Poor Oral Hygiene: Insufficient oral hygiene practices, including irregular brushing, inadequate flossing, or neglecting routine dental check-ups, contribute to the development of tooth infections. Failing to remove plaque and bacteria from the teeth and gums allows harmful microorganisms to prosper, leading to infections. Emphasizing the significance of consistent oral hygiene habits can significantly reduce the occurrence of dental infections.
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the causative factors and triggers behind dental infections, individuals can make informed decisions and take proactive measures to protect their oral health. Recognizing the role of microorganisms, addressing dental issues promptly, considering the impact of compromised immune systems, and prioritizing proper oral hygiene are essential in preventing and managing tooth infections effectively.
Recognizing the Typical Signs of a Decayed Tooth
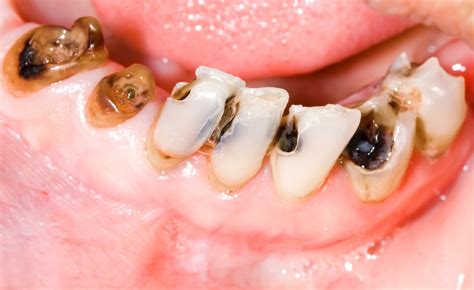
Overview: In this section, we will discuss the common indicators that may suggest the presence of a deteriorated tooth. It is crucial to recognize these symptoms promptly to ensure timely intervention and prevent further complications. Although each individual may experience varying degrees of discomfort, the following signs are generally seen in cases of tooth decay.
1. Oral Pain: One of the primary indications of a decayed tooth is persistent oral discomfort. This pain can range from mild to severe and may manifest as throbbing, sharp, or constant. It is often triggered by the consumption of certain foods and drinks, especially those that are hot, cold, or sweet. The intensity of the pain can fluctuate and may worsen when pressure is applied to the affected tooth.
2. Tooth Sensitivity: Sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures is a common symptom of tooth decay. Sudden twinges of pain may occur while consuming hot or cold beverages or during exposure to chilly air. Individuals with decayed teeth often experience discomfort when brushing or flossing, particularly at the site of the decay.
3. Discoloration: Discoloration of the affected tooth is an indicative sign of decay. The tooth may appear darker or develop noticeable stains, ranging from brown to black. This discoloration occurs as a result of the damage caused by decay, which affects the tooth's structure and color.
4. Bad Breath: Foul breath or persistent bad taste in the mouth can result from a decayed tooth. The accumulation of bacteria in the affected area can produce unpleasant odors, leading to chronic halitosis. If regular oral hygiene practices do not improve the breath, it may be a sign of tooth decay.
5. Swelling or Pus: In advanced cases of tooth decay, swelling and the presence of pus or a discharge may occur. This can indicate an abscess, which is a serious condition requiring immediate dental attention. Abscesses can cause extreme pain, gum inflammation, and even fever.
Conclusion: Recognizing the common symptoms associated with a decayed tooth is essential for early detection and appropriate treatment. Regular dental check-ups, along with maintaining good oral hygiene practices, can help prevent tooth decay and its subsequent complications. If any of these symptoms are experienced, it is recommended to consult a dental professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
The Risks of Ignoring an Ailing Tooth
One cannot underestimate the potential hazards associated with neglecting a compromised dental condition. Deliberately overlooking the signs of distress within the oral cavity can lead to grave consequences not only for the affected tooth but also for the overall well-being of the individual.
Putting off appropriate action when faced with a tooth ailment can exacerbate the existing condition, allowing it to progress unchecked. The ramifications of this neglect may manifest in a multitude of ways, ranging from localized pain and discomfort to systemic infections that can pose significant risks to one's health.
Inadequate attention to an ailing tooth may also result in the spread of harmful bacteria throughout the body, potentially leading to life-threatening complications. The infection originating from the untreated tooth can find its way into the bloodstream, allowing it to travel to vital organs and areas of vulnerability, such as the heart or the brain.
Furthermore, neglecting an infected tooth can have a substantial impact on an individual's quality of life. Persistent pain, difficulty in chewing and speaking, and a diminished ability to enjoy food can all affect one's overall well-being and interpersonal interactions.
While seeking professional dental care may require time, effort, and financial investment, ignoring an infected tooth can prove to be far costlier in the long run. The potential consequences of inaction should serve as a powerful motivator to prioritize oral health and promptly address any signs of dental distress.
Diagnosing an Ailing Tooth: Insights into Identifying the Problem
When encountering dental discomfort or persistent pain in your oral cavity, it becomes imperative to seek accurate identification and diagnosis to address the underlying issue. This section sheds light on what to expect during the diagnostic process of an ailing tooth, recognizing the signs, and understanding the steps involved in determining the problem.
Evaluating Dental Symptoms:
Diagnosing an ailing tooth often begins with a comprehensive evaluation of your dental symptoms. Dentists carefully observe and analyze indicators such as throbbing or sharp pain, sensitivity to hot and cold stimuli, swelling, facial tenderness, gum inflammation, and potential abscess formation. These symptoms provide valuable clues that aid in narrowing down the potential causes of the dental distress.
Clinical Examination:
Once preliminary symptom evaluation is complete, a dentist proceeds with a clinical examination of the affected tooth. This entails a thorough visual inspection using specialized tools and mirrors to detect visible signs of decay, fractures, or abscesses. They may also gently test the tooth's response to different stimuli to assess its sensitivity and potential nerve involvement.
Diagnostic Tests:
In some cases, additional diagnostic tests may be required to further investigate the problem. Dental X-rays are commonly employed to capture detailed images of the tooth, surrounding tissues, and underlying bone structure. These images enable dentists to detect hidden infections, bone loss, impacted teeth, and other issues that are not apparent during the clinical examination.
Collaborative Discussion:
After gathering all the necessary information, dentists engage in a collaborative discussion with the patient. This allows them to explain their findings, discuss potential diagnoses, and educate patients on the recommended treatment options. Open communication fosters a shared decision-making process, ensuring patients are actively involved in their dental care and are well-informed about the next steps to rectify the ailing tooth.
Referral to Specialists:
In complex cases or situations where specialized knowledge is required, dentists may choose to refer patients to dental specialists, such as endodontists or oral surgeons. These specialists possess advanced expertise in diagnosing and treating complicated dental conditions, ensuring that patients receive the most appropriate and effective care for their infected tooth.
With a comprehensive understanding of the diagnostic journey for an ailing tooth, individuals can approach dental appointments with confidence, knowing what to anticipate and expect throughout the process.
Available Treatment Options for Dental Infections
When it comes to managing and addressing dental infections, there are several effective treatment options available that can help alleviate the discomfort and prevent further complications. These treatment options encompass various approaches to tackle the underlying issues causing dental infections, providing relief and promoting oral health.
- Prescription Antibiotics: In cases where the dental infection is mild or localized, a dentist may prescribe antibiotics to help eliminate the bacterial infection. These antibiotics can effectively target and destroy the bacteria responsible for the infection, allowing the tooth and surrounding tissues to heal.
- Root Canal Treatment: For more severe dental infections, root canal treatment may be recommended. This procedure involves removing the infected pulp from the tooth, cleaning the root canal, and sealing it to prevent reinfection. Root canal treatment can salvage the natural tooth, alleviating pain and preventing the need for extraction.
- Tooth Extraction: In some cases, when the infection has extensively damaged the tooth and surrounding tissues, extraction may be necessary. Tooth extraction involves removing the infected tooth to prevent the spread of the infection to neighboring teeth. After extraction, options for tooth replacement, such as dental implants or bridges, can be explored.
- Drainage of Abscesses: In situations where an abscess has formed due to a severe dental infection, the dentist may need to perform a minor surgical procedure to drain the abscess. This helps relieve pain and pressure caused by the buildup of pus, facilitating the healing process.
- Improving Oral Hygiene: Maintaining proper oral hygiene practices is crucial in preventing and managing dental infections. Regular brushing, flossing, and using antimicrobial mouth rinses can help remove bacteria, plaque, and prevent the buildup of harmful substances that contribute to infections. Additionally, routine dental check-ups and cleanings can help identify and address early signs of dental infections.
It is essential to consult a dentist as soon as possible if you suspect a dental infection. They will assess the severity of the infection and determine the most appropriate treatment option to restore oral health and alleviate any discomfort you may be experiencing.
Preventive Measures to Avoid Dental Infections

Avoiding dental infections is crucial for maintaining good oral health. By following preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing infections in your teeth. These measures encompass various aspects of oral care, from cleaning habits to dietary choices.
Maintain Proper Oral Hygiene
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day using a fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth.
- Rinse your mouth with an antibacterial mouthwash to reduce bacteria presence.
- Regularly visit a dentist for professional cleanings and check-ups.
Watch Your Eating Habits
- Avoid consuming excessive sugary foods and drinks, as they promote bacterial growth.
- Opt for a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to support overall dental health.
- Limit acidic foods and beverages to prevent tooth enamel erosion.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
Take Care of Your Teeth and Gums
- Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and replace it regularly.
- Consider using an electric toothbrush for more effective cleaning.
- Be gentle while brushing to avoid gum irritation.
- Avoid habits like nail-biting and chewing on hard objects that can lead to cracked teeth.
Protect Your Teeth During Physical Activities
- Wear a mouthguard when participating in sports or high-risk activities to prevent dental injuries.
- Consult a dentist to get a customized mouthguard for enhanced protection.
By incorporating these preventive measures into your daily routine, you can minimize the risk of tooth infections, ensuring a healthy and pain-free smile. Remember, prevention is better than cure when it comes to dental health!
Seeking Professional Assistance for a Decaying Tooth
When faced with the challenges of a deteriorating dental condition, it is crucial to turn to skilled and experienced dental professionals for assistance. Left untreated, dental problems can worsen and lead to severe complications, impacting not only oral health but also overall well-being. Professional intervention is essential to identify and address the underlying causes of a decaying tooth, alleviate symptoms, and prevent further deterioration.
Understanding the Importance of Dental Expertise
Seeking the help of a dental professional is essential as they possess the knowledge, skills, and technology to accurately diagnose and treat dental infections and decay. These experts can identify the specific causes of tooth decay, such as poor oral hygiene, dental trauma, or underlying systemic conditions that may contribute to dental problems. By consulting with a dental professional, individuals can receive personalized treatment plans tailored to their unique needs, ensuring the most effective and efficient treatment outcomes.
Addressing Symptoms and Providing Relief
Experiencing symptoms associated with a decaying tooth, such as persistent toothache, sensitivity to temperature changes, and swelling, can be distressing and disrupt daily activities. Dental professionals have the expertise to address these symptoms promptly and provide relief through various techniques, including pain management, root canal therapy, or tooth extraction if necessary. Seeking professional help ensures that individuals receive appropriate treatment to alleviate discomfort and prevent further damage.
Preventing Further Tooth Damage
Aside from immediate symptom relief, dental professionals play a crucial role in preventing further tooth damage and preserving overall oral health. They can offer comprehensive advice on oral hygiene practices and provide guidance on proper brushing and flossing techniques, as well as recommend suitable preventive measures such as dental sealants or fluoride treatments. Regular dental check-ups allow professionals to monitor the progress of tooth decay, catch any potential issues early on, and implement proactive measures to prevent further decay and infection.
Conclusion
When faced with an ailing tooth, seeking professional dental assistance is paramount to address the underlying causes, alleviate symptoms, and prevent further deterioration. Dental professionals bring their expertise and technology to accurately diagnose and offer personalized treatments, ensuring the best outcomes for individuals facing dental problems. Remember, by seeking professional help, individuals can regain oral health and overall well-being, enjoying a pain-free and confident smile.
FAQ
What are the causes of an infected tooth?
An infected tooth can have several causes, including tooth decay, a cracked tooth, or a dental injury. Poor oral hygiene and a weakened immune system can also contribute to tooth infections.
What are the symptoms of an infected tooth?
The symptoms of an infected tooth may include severe toothache, sensitivity to hot and cold, swelling of the gums or face, bad breath, and a foul taste in the mouth. In more severe cases, there may be pus drainage or fever.
How is an infected tooth treated?
The treatment for an infected tooth depends on the severity of the infection. In many cases, a root canal procedure is performed to remove the infection from the tooth and save it. In more severe cases, extraction of the tooth may be necessary. Antibiotics are often prescribed to control the infection.
Can an infected tooth be prevented?
Proper dental hygiene is crucial in preventing tooth infections. Regular brushing and flossing, along with routine dental check-ups, can help identify and address dental issues before they become infected. Avoiding sugary foods and drinks can also help prevent tooth decay and subsequent infections.
Are there any complications associated with an untreated infected tooth?
Yes, leaving an infected tooth untreated can lead to various complications. The infection can spread to surrounding tissues, causing abscesses or cellulitis. In severe cases, the infection can even spread to other parts of the body, leading to potentially life-threatening conditions such as sepsis.



