Human mobility, an integral aspect of daily life, is intrinsically reliant on the sturdy framework of the vertebral column. Yet, far too often, individuals experience a perplexing predicament marked by an enigmatic break within this vital structure. This condition, often depicted as a surreal vision that shatters the harmony of one's physical being, encompasses a multitude of underlying factors that ignite its occurrence.
Origins: The genesis of this spinal disruption can be attributed to a plethora of diverse origins, extending from unforeseen traumatic incidents and strenuous physical exertion to underlying medical conditions that remain stealthily concealed. What sets this conundrum apart is its ability to transcend age, gender, and societal boundaries, rendering individuals vulnerable to its grip at any given moment.
Indications: The consequences of a compromised spinal column manifest themselves discreetly but relentlessly, burdening the victim with an assortment of telltale signs. Delicate whispers of discomfort gradually escalate into a symphony of acute pain, leading to restricted mobility, a limited range of motion, and an insidious compromise of daily activities. These indicators, often disguised as inconspicuous discomfort, serve as crucial alarm bells demanding swift attention and decisive action.
Remedies: While the path to recovery may appear as an insurmountable obstacle, modern medicine has devised a multitude of innovative interventions aimed at alleviating the anguish and facilitating the intricate healing process. From conservative treatments encompassing physical therapy, pain management, and lifestyle modifications, to more drastic measures such as surgical interventions and spinal fusion, countless options await those pursuing restoration of their disrupted backbone.
In conclusion, uncovering the enigma of a fractured spine necessitates a comprehensive understanding of its origins, a keen eye for its subtle indications, and a proactive approach towards exploring the myriad of available remedies. By embarking on this journey, individuals afflicted by this elusive condition can strive for the reinstatement of their once harmonious physical balance and rediscover the vast expanse of possibilities that lie beyond.
Understanding Spinal Fractures: Causes and Risk Factors
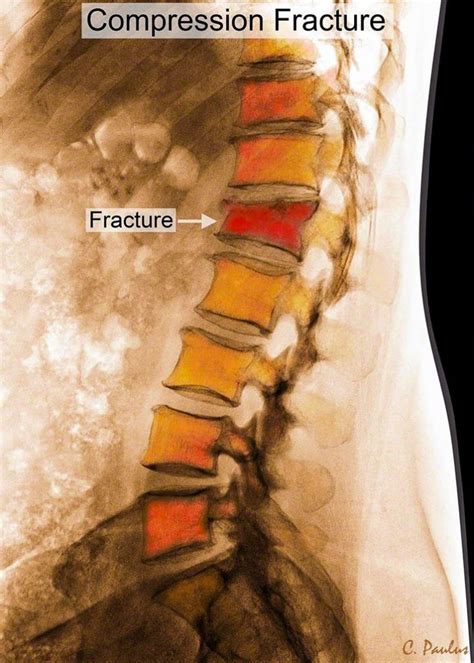
A spinal fracture is a serious injury that can lead to significant pain and disability. It occurs when one or more of the bones in the spine break or fracture. Spinal fractures can be caused by various factors and understanding these causes and risk factors is crucial in prevention and effective treatment.
Several common causes of spinal fractures include trauma, such as falls or car accidents, osteoporosis, cancer, and certain medical conditions that weaken the bones. Trauma-related spinal fractures often occur as a result of a forceful impact to the spine, while fractures associated with osteoporosis are typically due to weakened and brittle bones. Additionally, cancerous tumors in the spine can weaken the vertebrae, leading to fractures, and certain medical conditions like osteogenesis imperfecta can increase the risk of spinal fractures.
Risk factors that contribute to the development of spinal fractures include age, gender, lifestyle choices, and underlying medical conditions. As age increases, the risk of spinal fractures also rises, as older individuals have a higher likelihood of having decreased bone density. Women are more prone to spinal fractures due to the decrease in estrogen levels after menopause, which contributes to bone loss. Lifestyle choices, such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, can weaken the bones and increase the risk of fractures. Certain medical conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and hyperparathyroidism can also predispose individuals to spinal fractures.
Understanding the causes and risk factors of spinal fractures is crucial for effective prevention and management. By identifying individuals at higher risk, preventive measures, such as proper nutrition, exercise, and fall prevention strategies, can be implemented. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment plans can also minimize pain, promote healing, and prevent further complications associated with spinal fractures.
- Spinal fractures result from various causes, including trauma, osteoporosis, cancer, and medical conditions.
- Common risk factors for developing spinal fractures include age, gender, lifestyle choices, and certain underlying medical conditions.
- Preventive measures, early diagnosis, and appropriate treatment are essential in managing spinal fractures and reducing associated complications.
Recognizing the Signs: Symptoms Associated with Spinal Fractures
When it comes to the human body, especially the spine, it is crucial to be aware of potential injuries and their presenting symptoms. Being able to recognize the signs of a spinal fracture, or a broken back, can help individuals seek appropriate medical attention and commence timely treatment. Understanding the various symptoms associated with this condition is essential in ensuring early diagnosis and management, as well as preventing further complications.
| Common Symptoms | Less Common Symptoms |
|---|---|
|
|
It is important to note that the specific symptoms experienced may vary depending on the location and severity of the spinal fracture. Furthermore, some individuals may not experience any symptoms, especially in cases of mild fractures or stress fractures. However, any suspicion of a broken back should be taken seriously and prompt medical evaluation should be sought to determine the appropriate course of action.
In the next section, we will explore the potential causes of spinal fractures and how they can be effectively treated to promote healing and recovery.
Diagnosis Techniques: Identifying Spinal Fractures
When it comes to spinal fractures, accurate diagnosis is crucial in order to determine the appropriate course of treatment. This section explores the various techniques that doctors employ to identify and diagnose spinal fractures without relying on specific details.
1. Medical History: Doctors begin by gathering a comprehensive medical history of the patient, including previous injuries or conditions that may have predisposed them to spinal fractures. This initial step helps create a baseline understanding of the patient's overall health and any potential risk factors.
2. Physical Examination: A thorough physical examination is conducted to assess the patient's range of motion, reflexes, and any signs of tenderness or swelling in the affected area. Doctors pay close attention to the spine's alignment and note any abnormalities that may indicate a fracture.
3. Imaging Tests: To obtain a definitive diagnosis, doctors typically rely on imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans. These tests provide detailed images of the spine, allowing doctors to visualize fractures, assess their severity, and determine the most appropriate treatment approach.
4. Bone Scans: In some cases, doctors may recommend bone scans to assess the overall bone health and identify any other potential fractures. This technique involves injecting a small amount of radioactive substance into the patient's bloodstream, which then accumulates in areas of increased bone activity, highlighting any potential fracture sites.
5. Biopsy: In rare instances where the diagnosis remains unclear, doctors may perform a biopsy. This involves extracting a small tissue sample from the affected area of the spine to examine it under a microscope. A biopsy can help confirm the presence of a spinal fracture and rule out any other underlying conditions.
To accurately diagnose spinal fractures, doctors employ a combination of medical history analysis, physical examinations, and imaging tests. The integration of different diagnostic techniques allows healthcare professionals to develop an informed treatment plan tailored to the individual needs of the patient.
Healing Fractured Spines: Surgical and Non-surgical Options for Recovery
In this section, we will explore the various treatment options available for individuals who have suffered a fracture in their spinal vertebrae. Whether you have experienced a spinal injury or know someone who has, understanding the different approaches to healing a broken back can be crucial in facilitating the recovery process.
| Treatment Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Non-surgical Treatments | Utilizing conservative methods, non-surgical treatments aim to manage pain, promote natural healing, and improve mobility without the need for invasive procedures. These approaches may include physical therapy, pain medication, and bracing. |
| Surgical Treatments | When more severe fractures or complications arise, surgical intervention may be necessary to stabilize the broken vertebrae and facilitate proper healing. Surgical options can range from minimally invasive techniques, such as spinal fusion, to more complex procedures like vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty. |
Each treatment approach has its own set of advantages, disadvantages, and considerations. While non-surgical methods may be preferred for less severe fractures, surgical treatments provide a more direct and immediate solution for critical cases. It is crucial to consult with a medical professional to determine the most suitable treatment plan based on your specific condition and needs.
Additionally, the success of recovery depends on factors such as the location and severity of the fracture, overall health, age, and lifestyle. Rehabilitation, post-treatment care, and regular follow-up appointments also play a significant role in attaining optimal outcomes and preventing further complications.
Rehabilitation and Recovery: Steps to Restoring Mobility after a Spinal Fracture

Following a spinal fracture, undergoing a comprehensive rehabilitation program is crucial in rebuilding strength, regaining mobility, and improving overall quality of life. This section focuses on the essential steps involved in the rehabilitation and recovery process, aiming to provide individuals with a clear understanding of the journey towards restoring movement and function in the spine.
- Evaluation and assessment: A thorough assessment is conducted by healthcare professionals to determine the extent of the spinal fracture, identify any associated injuries, and assess the patient's overall physical condition. This evaluation helps create a personalized rehabilitation plan.
- Pain management: Effective pain management strategies are implemented to alleviate discomfort and promote a conducive environment for the rehabilitation process. Medications, physical therapy modalities, and other interventions may be used to address pain.
- Mobility restoration exercises: Specialized exercises are prescribed to gradually improve mobility in the spine. These exercises focus on strengthening the surrounding muscles, improving flexibility, and enhancing mobility within safe limits.
- Assistive devices and adaptive techniques: Depending on the severity of the spinal fracture and the individual's specific needs, assistive devices such as braces, walkers, or canes may be recommended to support mobility during the recovery period. Additionally, adaptive techniques may be taught to assist with daily activities.
- Physical therapy: Professional guidance from physical therapists plays a vital role in the recovery process. Physical therapy sessions involve a combination of manual therapy techniques, exercises, and stretches to enhance mobility, address imbalances, and promote proper body mechanics.
- Gradual progression: Rehabilitation following a spinal fracture is a gradual process. As the individual's condition improves, rehabilitation activities are modified and progressed accordingly, with the primary focus on regaining full mobility and function in the spine.
- Psycho-emotional support: Coping with a spinal fracture and the associated limitations can be mentally and emotionally challenging. Counseling, support groups, or individual therapy sessions may be beneficial in addressing any psychological concerns and promoting overall well-being.
- Long-term maintenance: After completion of the rehabilitation program, maintaining a regular exercise routine and following a healthy lifestyle become essential in sustaining the improvements achieved. Periodic evaluations with healthcare professionals may also be recommended to monitor progress and address any potential issues.
By following these crucial steps and working closely with healthcare professionals, individuals can maximize their chances of regaining mobility and achieving a successful recovery following a spinal fracture.
FAQ
What are the causes of a broken back?
A broken back, also known as a spinal fracture, can be caused by traumatic injury such as car accidents, falls, or sports injuries. It can also be a result of osteoporosis, a condition that weakens the bones, making them more susceptible to fractures.
What are the common symptoms of a broken back?
The symptoms of a broken back can vary depending on the severity and location of the fracture. Common symptoms include severe back pain that worsens with movement, swelling, bruising, numbness or tingling sensation, difficulty walking or standing, and in severe cases, loss of control over bladder or bowel function.
How is a broken back diagnosed?
A broken back is typically diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history review, and imaging tests. Doctors may perform X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans to get a detailed view of the spine and identify any fractures or other abnormalities.
What are the treatment options for a broken back?
The treatment for a broken back depends on the severity of the fracture. In some cases, conservative treatments such as rest, pain medications, and physical therapy may be sufficient. However, more severe fractures may require immobilization with braces or casts, or even surgery to realign and stabilize the spine.



